Linux:父子进程使用共享内存通信,包含创建和释放共享内存操作
迪丽瓦拉
2025-05-28 15:53:17
0次
测试程序:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#if 0
int main(void *arg)
{
int shmid = -1;
shmid = shmget(0x0002, 256, 0644 | IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL);//获取内存分配的进程id
if (-1 == shmid)
{perror("create shm failed ...");return(-1);
}printf("create shm ok\n");char *buf = NULL;
buf = (char *)shmat(shmid, NULL, SHM_RND); //共享内存同进程关联,并获取共享内存文件描述符buf.
if ((char *)-1 == buf)
{perror("shmat failed ...");return(-1);
}memcpy(buf, "hello world", sizeof("hello world"));printf("buf is: %s\n", buf);getchar(); //暂停一下进程,回车键继续执行shmdt(buf);//shimid共享内存同进程脱离printf("finish dt \n");getchar();//暂停一下进程,回车键继续执行int ret = shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL); //把shimid共享内存标志为即将删除,当操作过它的进程都退出时,系统会删除该共享内存
if ((void *)-1 == buf)
{perror("shmctl failed ...");return(-1);
}return 0;
}
#endif
#if 1
int main(int * argc, const char * argv[])
{
key_t key = IPC_PRIVATE;
int shmid = shmget(0x1002, 512, 0644 |IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL);
if(shmid == -1) perror(“shmget fail with: \n”);
char *shmfp = NULL;
shmfp = (char *)shmat(shmid, NULL, SHM_RND);
memcpy(shmfp,“hello world”,sizeof(“hello world”));
printf(“shmfp content is: %s\n”, shmfp);
int i = 0;
pid_t pid;
for(i =0; i < 2; i++)
{pid = fork();if(pid == 0) break;
}
if(pid == 0) //子进程逻辑
{if(i == 0) {memcpy(shmfp,"child0 say hello world",sizeof("child0 say hello world"));printf("shmfp content is: %s\n", shmfp);} else if(i == 1){memcpy(shmfp,"child1 say hello world",sizeof("child1 say hello world"));printf("shmfp content is: %s\n", shmfp); }} else if(pid > 0)
{memcpy(shmfp,"father say hello world",sizeof("father say hello world"));printf("shmfp content is: %s\n", shmfp); }
if(pid == 0)
{getchar(); //暂停一下进程,回车键继续执行shmdt(shmfp);//shimid共享内存同进程脱离printf("pid %d finish dt \n", getpid());getchar();//暂停一下进程,回车键继续执行int ret = shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL); //把shimid共享内存标志为即将删除,当操作过它的进程都退出时,系统会删除该共享内存printf("pid %d finish 把shimid共享内存标志为即将删除 \n", getpid());if ((void *)-1 == shmfp){perror("shmctl failed ...");return(-1);}
}
if(pid > 0) //父进程退出前回收子进程
{ while(1) {sleep(1);int status = -1;//int ret = waitpid(-1,&status,WNOHANG);int ret = wait(&status);//阻塞等待子进程退出if(WIFEXITED(status)) printf("recycle child , status:%d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));if(WIFSIGNALED(status)) printf("recycle child , with status:%d\n", WTERMSIG(status));if(status == 0) break;//当status为0时,子进程回收完毕,父进程退出循环。}getchar(); //暂停一下进程,回车键继续执行shmdt(shmfp);//shimid共享内存同进程脱离printf("pid %d finish dt \n", getpid());getchar();//暂停一下进程,回车键继续执行int ret = shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL); //把shimid共享内存标志为即将删除,当操作过它的进程都退出时,系统会删除该共享内存printf("pid %d finish 把shimid共享内存标志为即将删除 \n", getpid());
}
return 0;
}
#endif
结果:
启动3个进程:
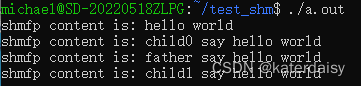
查看进程id

查看shm资源 nattch为3
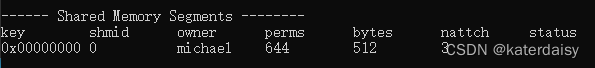
回车6次删除共享内存,nattch引用依次减小。
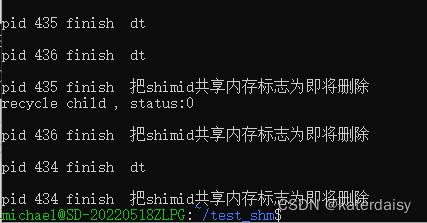
三个进程运行结束后共享内存资源被释放

相关内容
热门资讯
Linux-scheduler...
四、调度域 SDTL结构 linux内核使用SDTL结构体来组织CPU的层次关系 struct sc...
Retinanet网络与foc...
参考代码:https://github.com/yhenon/pytorch-reti...