蓝桥杯集训·每日一题Week3
Trie
AcWing 835. Trie字符串统计(算法基础课)

思路:
Trie是一种高效地存储和查找字符串集合的数据结构,适用于字符串不太复杂的情况。其形状是一个以0为根节点的树,查询和插入的效率都比较高,有插入和查询两种操作。Trie树通常用一个二维数组来存储,第一维表示节点的数量,第二维表示节点的状态数。
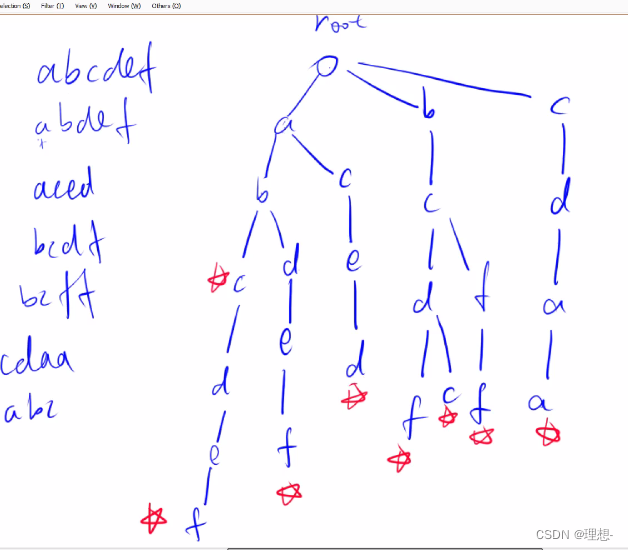
代码:
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 100005;// son存储trie树,以0为根节点的树,cnt存储字符串个数
int son[N][26], cnt[N], idx;
char str[N];void insert(char* str)
{// 祖宗节点int p = 0;for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++){int u = str[i] - 'a';// 子节点不存在就创建if (!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++idx;// 往下遍历trie树p = son[p][u];}// 该字符串个数加一cnt[p]++;
}int query(char* str)
{int p = 0;for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++){int u = str[i] - 'a';// 子节点不存在表示不包含当前字符串,返回0if (!son[p][u]) return 0;// 往下遍历trie树p = son[p][u];}// 返回字符串个数return cnt[p];
}int main()
{int n;cin >> n;while (n--){char op[2];scanf("%s%s", op, str);if (op[0] == 'I') insert(str);else printf("%d\n", query(str));}return 0;
}
思路:
把每一个整数看作一个二进制数来处理,按照字符串的形式插入到trie树中。要求找到一个异或后尽可能大的树,则要尽量使参与异或运算的两个数对应的位一个为0一个为1。在查询的过程中查找对应位不一样的数,如果有,则选择对应位不一样的数,否则选择对应位一样的数。
代码
#include
#includeusing namespace std;const int N = 100010, M = 31 * N;int a[N], son[M][2];
int n, idx;void insert(int x)
{int p = 0; // for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i--){int u = x >> i & 1; // 取二进制数的某一位的值if (!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++idx; // 如果下标为p的点的u(0或1)这个儿子不存在,那就创建p = son[p][u];}
}int query(int x)
{int p = 0, ret = 0;for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i--){int u = x >> i & 1;// 找对应位不一样的数,如果有则继续查找if (son[p][!u]){p = son[p][!u];ret = ret * 2 + !u; }// 退而求其次else{p = son[p][u];ret = ret * 2 + u;}}return ret;
}int main()
{cin >> n;int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){scanf("%d", &a[i]);insert(a[i]);int t = query(a[i]);res = max(res, t ^ a[i]);}cout << res << endl;return 0;
} 注意:
query函数有查询与当前值异或后最大的数,和最大的异或值两种写法。
int query(int x)
{int p = 0, ret = 0;for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i--){int u = x >> i & 1;// 找对应位不一样的数,如果有则继续查找if (son[p][!u]){p = son[p][!u];ret = ret * 2 + !u; }// 退而求其次else{p = son[p][u];ret = ret * 2 + u;}}return ret;
}int t = query(a[i]);
res = max(res, t ^ a[i]);
或者
int query(int x)
{int p = 0, ret = 0;for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i--){int u = x >> i & 1;// 找对应位不一样的数,如果有则继续查找if (son[p][!u]){p = son[p][!u];// 有不一样的当前位就取1ret = ret * 2 + 1; }// 退而求其次else{p = son[p][u];// 否则当前位取0ret = ret * 2;}}return ret;
}res = max(res, query(a[i]));
两种写法没有本质的区别。
AcWing 143. 最大异或对(算法基础课)
AcWing 3485. 最大异或和(每日一题)
思路:
对于区间的异或和问题,可以用前缀异或和数组进行优化。
要求 l∼rl\sim rl∼r之间的异或和,可以用 s[l−1]⊕s[r]s[l - 1] \oplus s[r]s[l−1]⊕s[r] 来实现。
本题有区间长度的限制,考虑滑动窗口,经过分析要实现三种操作。
- 插入一个数
- 删除一个数,假设区间长度为 mmm ,某尾为 iii, 则区间开端为 i−m+1i-m+1i−m+1,
s[i−m+1∼i]=s[i−m]⊕s[i]s[i-m+1 \sim i] = s[i - m] \oplus s[i]s[i−m+1∼i]=s[i−m]⊕s[i]则要把 区间外的数删除,即 s[i−m−1]s[i-m-1]s[i−m−1]。 - 查询最大的异或值
因此本题可以用Trie来实现。
代码:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;/*** @Description* @Author: PrinceHan* @CreateTime: 2023/2/27 10:28*/
public class Main {static final int N = 100005, M = 31 * N;// sum 前缀异或和数组 cnt记录当前节点有多少个数// [L,R]的异或和 = sum[L-1] ^ sum[R];static int[] sum = new int[N], cnt = new int[M];static int[][] son = new int[M][2];static int n, m, idx;public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));String[] nm = in.readLine().split(" ");n = Integer.parseInt(nm[0]);m = Integer.parseInt(nm[1]);String[] s = in.readLine().split(" ");for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){int x = Integer.parseInt(s[i - 1]);sum[i] = sum[i - 1] ^ x;}int res = 0;//边界 当所求得区间范围为1 ~ ? 时,需要用到sum[0]insert(sum[0], 1);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {// 如果i大于m,所用的数据为sum[i - m] ~ sum[i], 把区间外的删除if (i > m) insert(sum[i - m - 1], -1);res = Math.max(res, query(sum[i]));// 插入该数insert(sum[i], 1);}out.println(res);out.flush();}// v取值为:1 插入这个数,-1 删除这个数public static void insert(int x, int v) {int p = 0;for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--) {int u = x >> i & 1;if (son[p][u] == 0) son[p][u] = ++idx;p = son[p][u];cnt[p] += v;}}public static int query(int x) {int p = 0, sum = 0;for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--) {int u = x >> i & 1;if (cnt[son[p][1 - u]] != 0){sum = 2 * sum + 1;p = son[p][1 - u];}else {sum = 2 * sum;p = son[p][u];}}return sum;}
}BFS
AcWing 1562. 微博转发(每日一题)
思路:
本题本质上是求到某一点距离小于等于 lll 的点数,因此可以用 bfsbfsbfs 来求得当前点到其他点的距离,如果小于等于 lll ,答案 + 1。
代码:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Arrays;/*** @Description* @Author: PrinceHan* @CreateTime: 2023/3/1 7:59*/
public class Main {static final int N = 1005, M = N * 100;static int[] h = new int[N];static int[] e = new int[M];static int[] ne = new int[M];static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];static int n, l, idx;public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));Arrays.fill(h, -1);String[] nl = in.readLine().split(" ");n = Integer.parseInt(nl[0]);l = Integer.parseInt(nl[1]);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {String[] userList = in.readLine().split(" ");int un = userList.length;for (int j = 1; j < un; j++) {int u = Integer.parseInt(userList[j]);add(u, i);}}String[] q = in.readLine().split(" ");for (int i = 1; i < q.length; i++) {int t = bfs(Integer.parseInt(q[i]));out.println(t);}out.flush();}private static int bfs(int u) {Arrays.fill(st, false);int[] d = new int[N];int[] q = new int[N];int hh = 0, tt = -1;d[u] = 0;q[++tt] = u;st[u] = true;int cnt = 0;while (hh <= tt) {int v = q[hh++];for (int i = h[v]; ~i != 0; i = ne[i]) {int j = e[i];if (!st[j]) {st[j] = true;d[j] = d[v] + 1;if (d[j] <= l) {cnt++;q[++tt] = j;}}}}return cnt;}public static void add(int a, int b) {e[idx] = b;ne[idx] = h[a];h[a] = idx++;}
}
AcWing 844. 走迷宫(算法基础课)
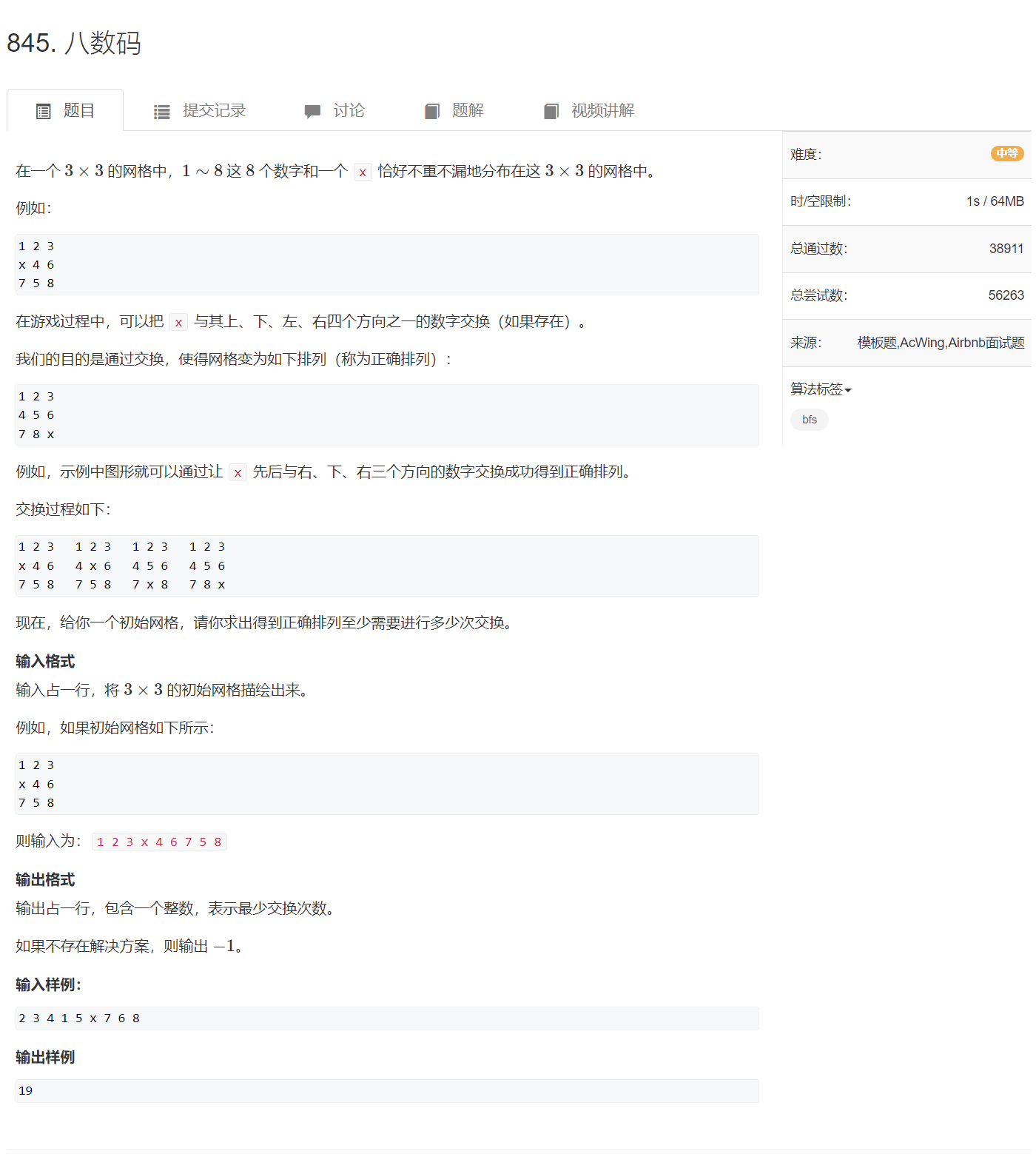
思路:
求正确排列的最小交换次数,可以想到用 bfsbfsbfs 来做。把一维的字符串抽象为一个二维的字符矩阵,每次交换 xxx 与上下左右四个方向的字符并且交换的次数,当交换后的结果为所需形式时,就结束 bfsbfsbfs,存储字符串和相应的交换次数可以用哈希表实现。
代码:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.*;/*** @Description* @Author: PrinceHan* @CreateTime: 2023/3/18 20:02*/
public class Main {static String end = "12345678x";static int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};public static int bfs(String str) {HashMap d = new HashMap<>();Queue q = new LinkedList<>();q.offer(str);d.put(str, 0);while (!q.isEmpty()) {String t = q.poll();int dt = d.get(t);if (t.equals(end)) return dt;char[] s = t.toCharArray();int loc = t.indexOf("x");int x = loc / 3, y = loc % 3;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int tx = x + dx[i], ty = y + dy[i];if (tx >= 0 && tx < 3 && ty >= 0 && ty < 3) {// 通过交换字符改变字符串结构,最后要换回来char c = s[loc];s[loc] = s[tx * 3 + ty];s[tx * 3 + ty] = c;String s1 = new String(s);if (!d.containsKey(s1)) {q.offer(s1);d.put(s1, dt + 1);}c = s[loc];s[loc] = s[tx * 3 + ty];s[tx * 3 + ty] = c;}}}return -1;}public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));String s = in.readLine();String s1 = "";int len = 0;for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {if (s.charAt(i) != ' ') s1 += s.charAt(i);}int res = bfs(s1);out.println(res);out.flush();}
}
AcWing 1233. 全球变暖(蓝桥杯辅导课)
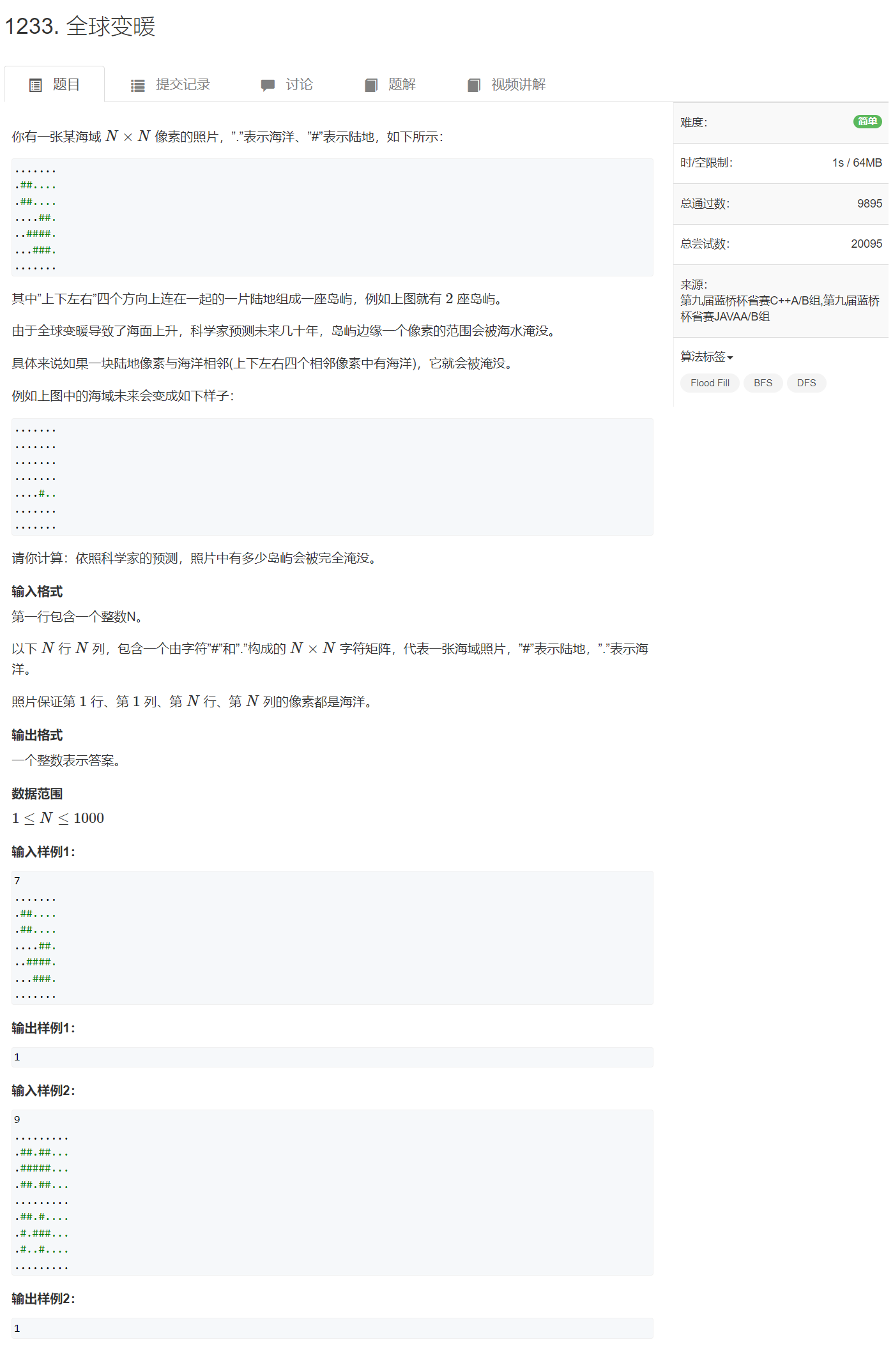
思想:
当一块陆地与一块海洋毗邻的时候,这块陆地就会被淹没。有多少陆地被淹没,等价于有多少个岛屿的陆地面积与海洋面积相同。因此,可以用 bfsbfsbfs 遍历图,记录一块岛屿的陆地个数以及相邻的海洋个数,如果陆地个数以及相邻的海洋个数相同的话,这个岛屿就会被淹没。
代码:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;/*** @Description* @Author: PrinceHan* @CreateTime: 2023/3/17 14:42*/
public class AC1233 {static final int N = 1010;static char[][] map = new char[N][N];static boolean[][] st = new boolean[N][N];static int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0,}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};static int[] q = new int[N * N];static int n;public static boolean bfs(int x, int y) {int hh = 0, tt = -1;int land_cnt = 0, sea_cnt = 0;q[++tt] = x * N + y;st[x][y] = true;while (hh <= tt) {int u = q[hh++];land_cnt++;int ux = u / N, uy = u % N;int flag = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int tx = ux + dx[i], ty = uy + dy[i];if (tx >= 0 && tx < n && ty >= 0 && ty < n) {if (map[tx][ty] == '.') flag = 1;if (map[tx][ty] == '#' && !st[tx][ty]) {q[++tt] = tx * N + ty;}}}if (flag == 1) sea_cnt++;}return land_cnt == sea_cnt;}public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {int ans = 0;BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));n = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {map[i] = in.readLine().toCharArray();}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if (!st[i][j] && bfs(i, j)) ans++;}}out.println(ans);out.flush();}
}
DFS
AcWing 3502. 不同路径数(每日一题)
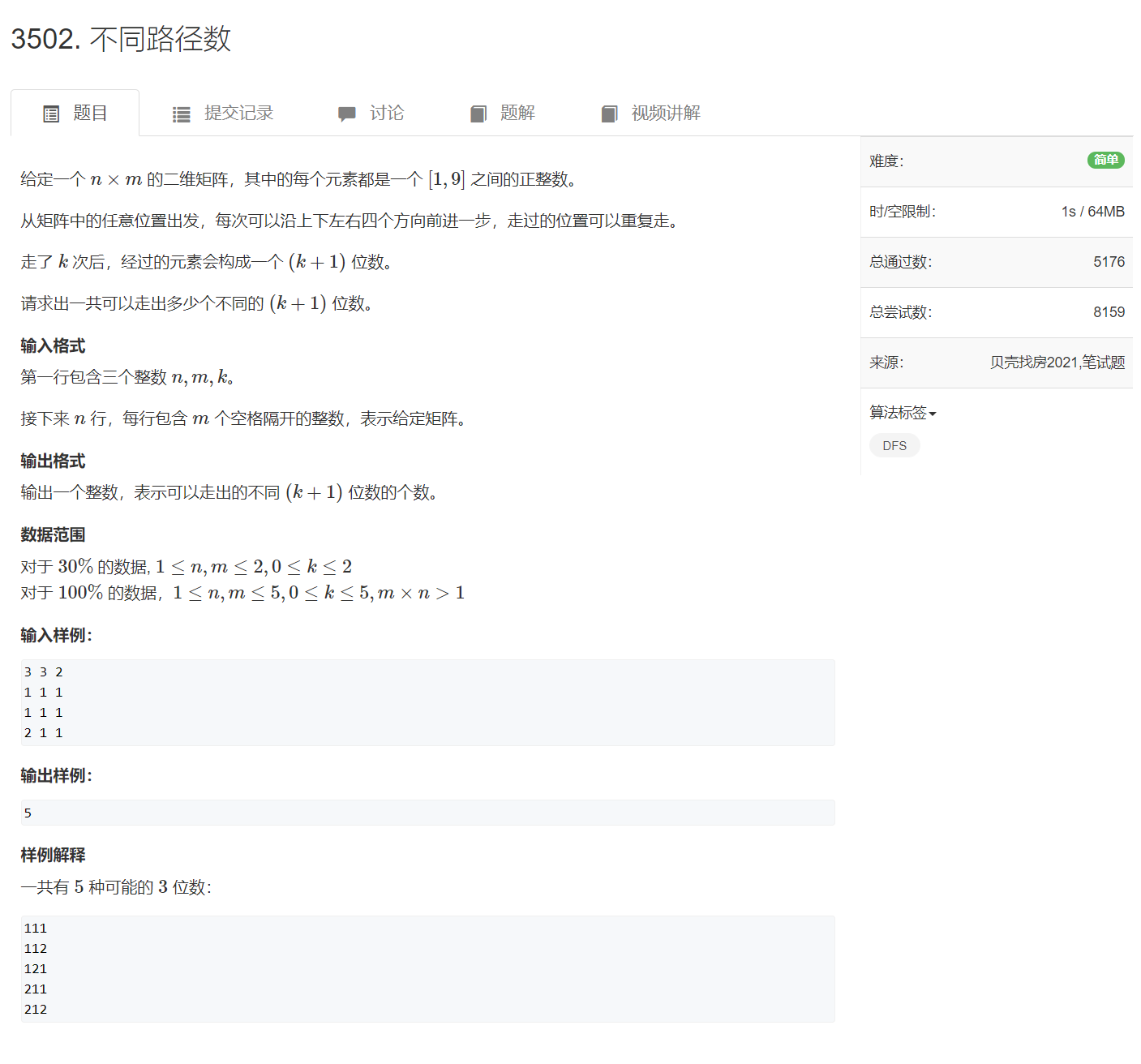
思路:
从每个位置出发开始搜素,因为走的位置可以重复,所以不需要做标记。当生成一个 k+1k+1k+1 位的数时,就加入到集合当中,最后输出集合的大小即可。
代码:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.TreeSet;/*** @Description* @Author: PrinceHan* @CreateTime: 2023/3/1 8:46*/
public class Main {static int[][] g = new int[10][10];static int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};static TreeSet nums = new TreeSet<>();static int n, m, k;static int num;public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));String[] nmk = in.readLine().split(" ");n = Integer.parseInt(nmk[0]);m = Integer.parseInt(nmk[1]);k = Integer.parseInt(nmk[2]);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {String[] tmp = in.readLine().split(" ");for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {g[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(tmp[j - 1]);}}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {dfs(i, j, 0, g[i][j]);}}out.print(nums.size());out.flush();}public static void dfs(int x, int y, int u, int start) {if (u == k) {nums.add(start);return;}for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int tx = x + dx[i], ty = y + dy[i];if (tx >= 1 && tx <= n && ty >= 1 && ty <= m) {dfs(tx, ty, u + 1, start * 10 + g[tx][ty]);}}}} AcWing 842. 排列数字(算法基础课)
代码
#include
using namespace std;int vis[10], a[10];void dfs(int step, int n)
{if (step == n + 1){for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)printf("%d ", a[i]);printf("\n");return;}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){if (!vis[i]) {a[step] = i;vis[i] = 1;dfs(step + 1, n);vis[i] = 0;}}
}int main()
{int n;scanf("%d", &n);dfs(1, n);return 0;
}
AcWing 843. n-皇后问题(算法基础课)
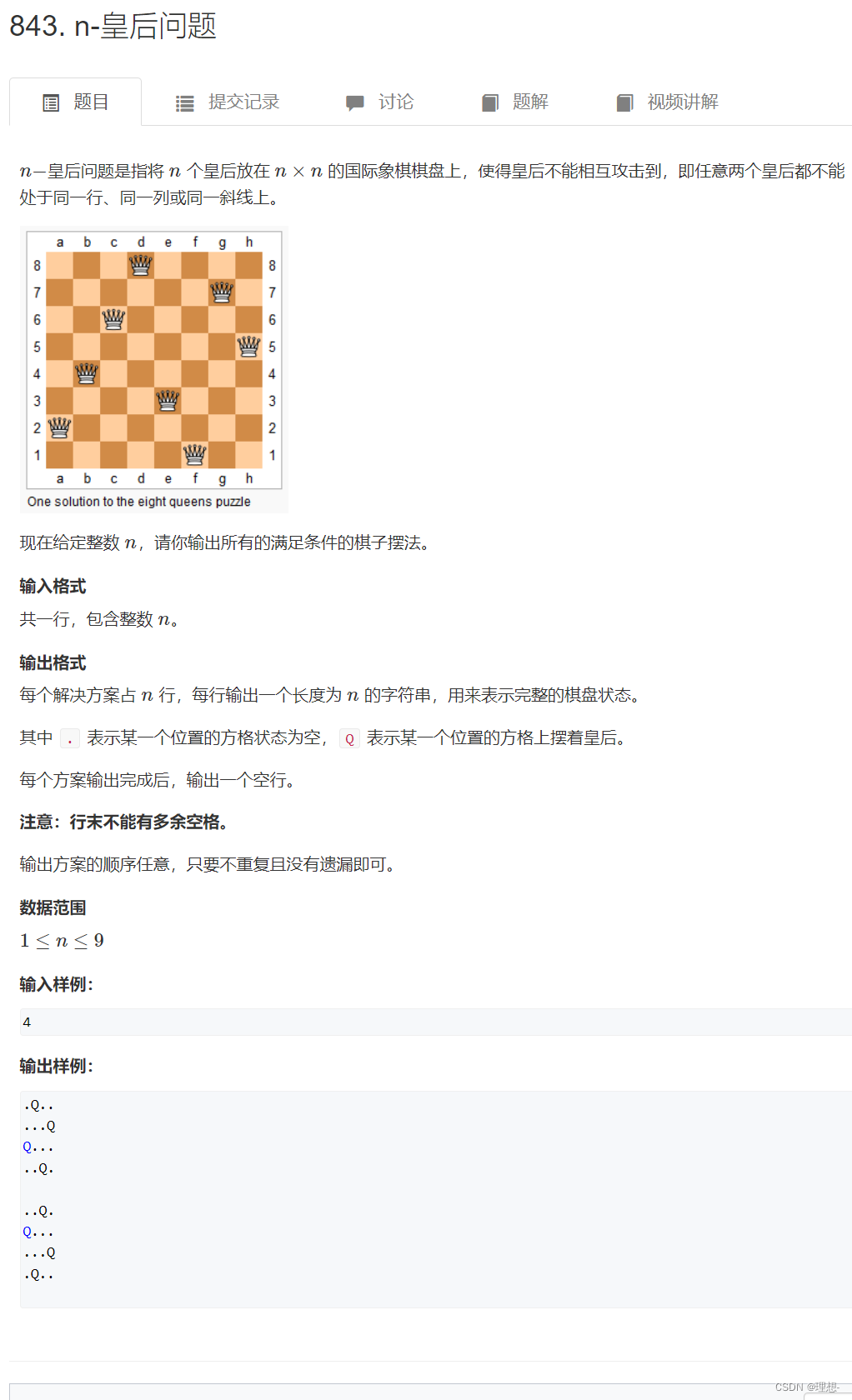
思路:
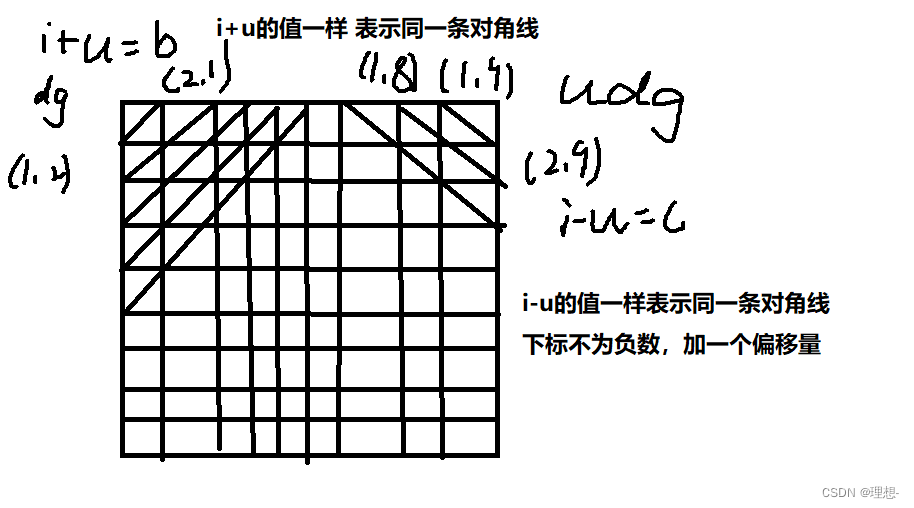
标记列,两个方向的对角线。
代码:
第一种搜索顺序
#include
using namespace std;const int N = 20;
bool col[N], dg[N], udg[N];
int n;
char g[N][N];void dfs(int u)
{if (u == n){for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) puts(g[i]);puts("");return;}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){if (!col[i] && !dg[i + u] && !udg[n + i - u]){g[u][i] = 'Q';col[i] = dg[i + u] = udg[n + i - u] = true;dfs(u + 1);col[i] = dg[i + u] = udg[n + i - u] = false;g[u][i] = '.';}}
}int main()
{scanf("%d", &n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)g[i][j] = '.';dfs(0);return 0;
}
第二种搜索顺序
标记行列,两个方向的对角线。
#include
using namespace std;const int N = 20;
bool row[N], col[N], dg[N], udg[N];
int n;
char g[N][N];void dfs(int x, int y, int s)
{if (y == n) y = 0, x++;if (x == n){if (s == n){for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) puts(g[i]);puts("");}return;}// 不放皇后dfs(x, y + 1, s);// 放皇后if (!row[x] && !col[y] && !dg[x + y] && !udg[n + x - y]){g[x][y] = 'Q';row[x] = col[y] = dg[x + y] = udg[n + x - y] = true;dfs(x, y + 1, s + 1);row[x] = col[y] = dg[x + y] = udg[n + x - y] = false;g[x][y] = '.';} }int main()
{scanf("%d", &n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)g[i][j] = '.';dfs(0, 0, 0);return 0;
}
AcWing 1209. 带分数
思路:
方法一: 暴力枚举全排列,枚举 aaa, bbb , ccc。枚举 aaa, bbb , ccc过程中配以剪枝, aaa的位数不超过6位。
代码:
import java.util.Scanner;/*** @Description* @Author: PrinceHan* @CreateTime: 2023/2/23 10:08*/
public class Main {static final int N = 15;static int ans;static int n;static int[] arr = new int[N];static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];static BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);n = scanner.nextInt();dfs(1);System.out.println(ans);}public static int cal(int a, int b) {int sum = 0;for (int i = a; i <= b; i++) sum = sum * 10 + arr[i];return sum;}public static void dfs(int u) {if (u > 9) {// 枚举a, b, cfor (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {for (int j = i + 1; j <= 8; j++) {int a = cal(1, i);int b = cal(i + 1, j);int c = cal(j + 1, 9);if (a * c + b == n * c) ans++;}}return;}for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {if (!st[i]) {arr[u] = i;st[i] = true;dfs(u + 1);st[i] = false;}}}
}方法二: 枚举 aaa, ccc。计算 bbb ,判断该组合是否不重不漏用完 1∼91\sim 91∼9 中的所有数。
代码:
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;/*** @Description* @Author: PrinceHan* @CreateTime: 2023/2/23 14:27*/
public class Main {static final int N = 15;static boolean[] st = new boolean[N], backup = new boolean[N];static int n, ans;public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);n = scanner.nextInt();dfs_a(0, 0);System.out.println(ans);}public static void dfs_a(int u, int a) {// 如果 a >= n 不满足条件 剪枝if (a >= n) return;// 在 a的基础上枚举cif (a != 0) dfs_c(u, a, 0);for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {if (!st[i]) {st[i] = true;dfs_a(u + 1, a * 10 + i);st[i] = false;}}}public static void dfs_c(int u, int a, int c) {if (u > 9) return;if (check(a, c)) ans++;for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {if (!st[i]) {st[i] = true;dfs_c(u + 1, a, c * 10 + i);st[i] = false;}}}public static boolean check(int a, int c) {// 防止爆 intlong b = n * (long) c - (long)a * c;if (a * b * c == 0) return false;for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {backup[i] = st[i];}while (b != 0) {long x = b % 10;b /= 10;// 出现了0 或者b的数字与 a c 的有重复 不满足条件if (x == 0 || backup[(int)x]) return false;backup[(int)x] = true;}// 保证每个数字都用过了for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {if (!backup[i]) return false;}return true;}
}
拓扑排序
AcWing 3696. 构造有向无环图(每日一题)
思路:
本题中的边分为两种,一种是确定了方向的有向边,另一种就是无向边。如果当前的有向边可以构成拓扑序列,通过确定无向边的方向也可以构成拓扑排序;否则就不可构成拓扑序列。
在有向边可构成拓扑序列的情况下,通过确定无向边的方向来构造拓扑序列。
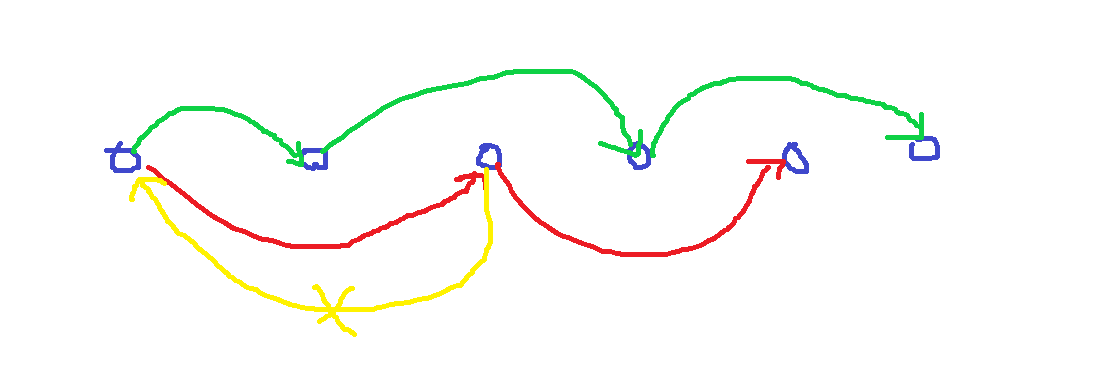
在有向边中已经建立好了的拓扑序列中,确定每一个点的顺序。如果有无向边的端点在拓扑序列中存在过,确定方向的话只需要从位置靠前的一点到位置靠后的一点连一条有向边即可;否则方向都可以。
代码:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StreamTokenizer;/*** @Description* @Author: PrinceHan* @CreateTime: 2023/3/2 19:01*/
public class Main {static final int N = 200005, M = N;static int[] h = new int[N];static int[] e = new int[M];static int[] ne = new int[M];static int[] ind = new int[N];static int[] q = new int[N];static int[] pos = new int[N];static int t, n, m, cnt, idx;static Edge[] edges = new Edge[N];static class Edge {int a, b;Edge(int a, int b) {this.a = a;this.b = b;}}static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));static StreamTokenizer in = new StreamTokenizer(br);static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {t = nextInt();while (t-- != 0) {idx = 0;// 无向边的个数cnt = 0;n = nextInt();m = nextInt();for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {h[i] = -1;ind[i] = 0;}for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {int t = nextInt();int x = nextInt();int y = nextInt();if (t == 1) {add(x, y);ind[y]++;} else {edges[cnt++] = new Edge(x, y);}}if (topSort()) {out.println("YES");// 输出有向边for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = h[i]; ~j != 0; j = ne[j]) {out.println(i + " " + e[j]);}}// 记录每个端点的位置for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) pos[q[i]] = i;// 处理无向边 端点位置靠前 -> 端点位置靠后for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {int a = edges[i].a, b = edges[i].b;if (pos[a] > pos[b]) out.println(b + " " + a);else out.println(a + " " + b);}} else {out.println("NO");}out.flush();}}public static int nextInt() throws IOException {in.nextToken();return (int)in.nval;}public static void add(int a, int b) {e[idx] = b;ne[idx] = h[a];h[a] = idx++;}public static boolean topSort() {int hh = 0, tt = -1;for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {if (ind[j] == 0) q[++tt] = j;}while (hh <= tt) {int v = q[hh++];for (int j = h[v]; ~j != 0; j = ne[j]) {int k = e[j];ind[k]--;if (ind[k] == 0) {q[++tt] = k;}}}return tt == n - 1;}
}
AcWing 848. 有向图的拓扑序列

分析
拓扑序列从入度为0的顶点开始,若去除该点到另一个点的边使得另一个点入度也为0,则这个点也应放到拓扑序列中,用队列来存储拓扑序列,若所有的点都在队列中,则存在拓扑序列,队列的序列即为拓扑序列,反之则不存在拓扑序列。
代码
#include
#include
using namespace std;const int N = 100010;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int q[N], in[N], hh, tt = -1;
int n, m;void add(int a, int b)
{e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}bool topsort()
{//将所有入度为0的点入队for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (!in[i]) q[++tt] = i;while (hh <= tt){int t = q[hh++];for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){int j = e[i];//去一条边 入度-1in[j]--;//入度为0 入队if (!in[j]) q[++tt] = j;}}return tt == n - 1;}int main()
{cin >> n >> m;memset(h, -1, sizeof h);while (m--){int a, b;cin >> a >> b;add(a, b);//点b的入度+1in[b]++;}if (topsort()){//拓扑序列就是队列的顺序for (int i = 0; i <= tt; i++) cout << q[i] << ' ';cout << endl;}else cout << -1;return 0;
}
Dijkstra
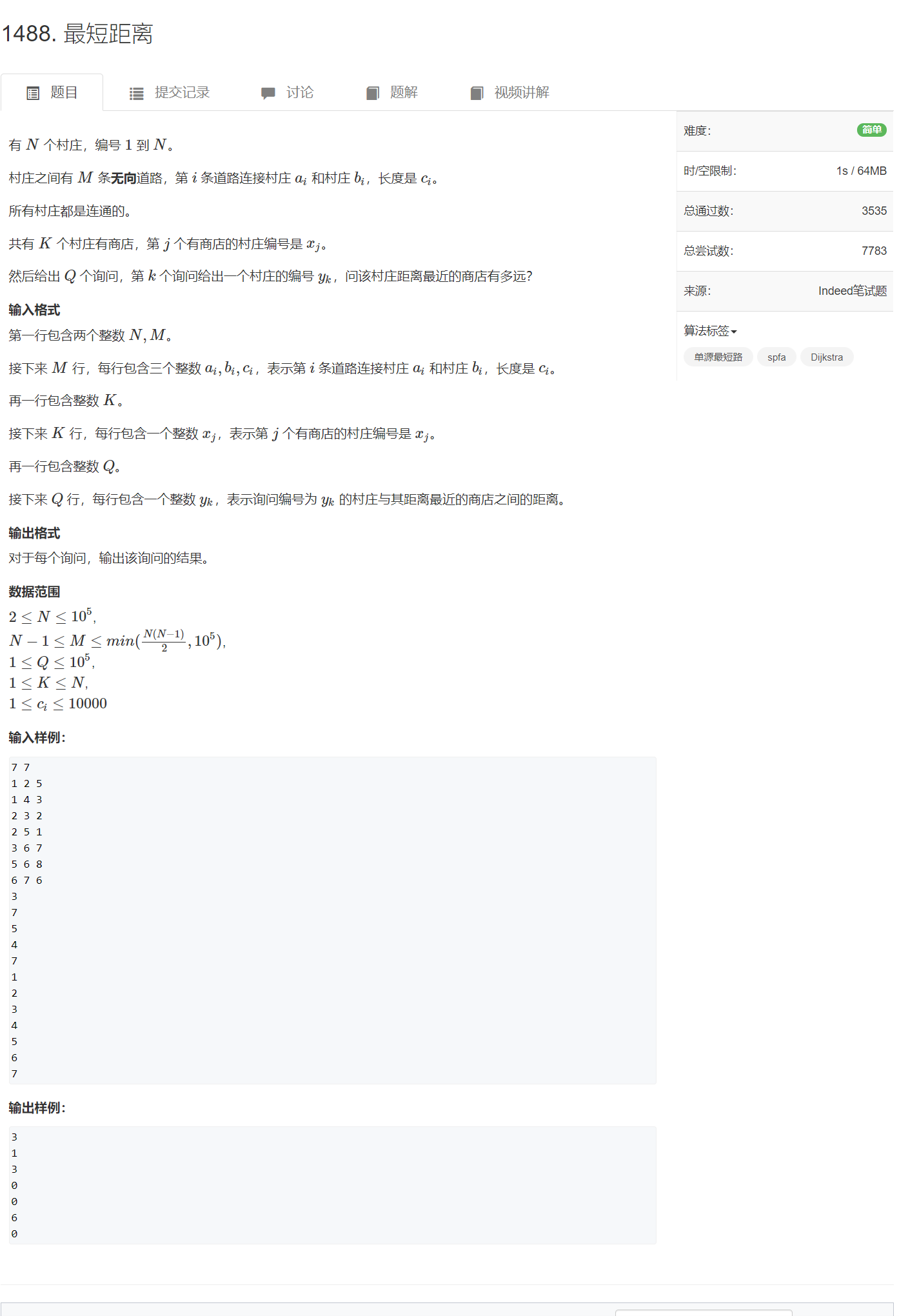
AcWing 1488. 最短距离(每日一题)
思路:
本题是一个最短路问题,可以用 spfaspfaspfa 或者 DijkstraDijkstraDijkstra 算法来解决。本题与一般的最短路问题不同之处在于 不是求某一点到一固定点的最短路径。有多个村庄,多个商店,求多个村庄到商店的最短路,如果把每一个商店作为源点来 spfaspfaspfa 或者 DijkstraDijkstraDijkstra 的话,会超时。因此,需要用到超级源点。
超级源点就是另找一个点,连接多个源点,并且超级源点到每个源点的路径长度为0。这样求多个村庄到商店的最短路问题可以转化为多个村庄到超级源点的距离,因此只要用一次 spfaspfaspfa 或者 DijkstraDijkstraDijkstra 即可。
对于 NNN 个点的无向图问题,邻接表要开到 2N2N2N,再加上超级源点,一共要开到 3N3N3N。
代码:
spfaspfaspfa
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StreamTokenizer;
import java.util.Arrays;/*** @Description* @Author: PrinceHan* @CreateTime: 2023/3/3 9:13*/
public class Main {/*** 数组要开大一点 点数为N的无向图,邻接表中e[] ne[] 的规模为2N, 加上超级源点一共是3N* 题目中给的N是10^5, 这里误开成了2 * 10^5, 阴差阳错也能满足范围*/static final int N = 200005, M = 2 * N;static int[] h = new int[N];static int[] e = new int[M];static int[] ne = new int[M];static int[] w = new int[M];static int[] d = new int[N];static int[] q = new int[M];static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];static int n, m, k, Q, y, idx;static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));static StreamTokenizer in = new StreamTokenizer(br);static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));public static int nextInt() throws IOException {in.nextToken();return (int)in.nval;}public static void add(int a, int b, int c) {e[idx] = b;ne[idx] = h[a];w[idx] = c;h[a] = idx++;}public static void spfa() {for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) d[i] = 0x3f3f3f3f;// 0为超级源点 连接所有商店,路径长度为0d[0] = 0;int hh = 0, tt = -1;q[++tt] = 0;st[0] = true;while (hh <= tt) {int t = q[hh++];st[t] = false;// 超级源点// 超级源点连接 商店// 连接村庄for (int i = h[t]; ~i != 0; i = ne[i]) {int j = e[i];if (d[j] > d[t] + w[i]) {d[j] = d[t] + w[i];if (!st[j]) {q[++tt] = j;st[j] = true;}}}}}public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {n = nextInt();m = nextInt();Arrays.fill(h, -1);while (m-- != 0) {int a = nextInt();int b = nextInt();int c = nextInt();add(a, b, c);add(b, a, c);}k = nextInt();// 连接超级源点和所有商店while (k-- != 0) {int x = nextInt();add(0, x, 0);}spfa();Q = nextInt();while (Q-- != 0) {y = nextInt();out.println(d[y]);}out.flush();}
}
DijkstraDijkstraDijkstra
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StreamTokenizer;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;/*** @Description* @Author: PrinceHan* @CreateTime: 2023/3/3 9:59*/
public class Main {static final int N = 200005, M = 2 * N;static int[] h = new int[N];static int[] e = new int[M];static int[] ne = new int[M];static int[] w = new int[M];static int[] d = new int[N];static int[] q = new int[M];static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];static int n, m, k, Q, y, idx;static class Edge {int d, v;Edge(int d, int v) {this.d = d;this.v = v;}}static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));static StreamTokenizer in = new StreamTokenizer(br);static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));public static int nextInt() throws IOException {in.nextToken();return (int)in.nval;}public static void add(int a, int b, int c) {e[idx] = b;ne[idx] = h[a];w[idx] = c;h[a] = idx++;}public static void dijkstra() {for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) d[i] = 0x3f3f3f3f;d[0] = 0;PriorityQueue heap = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(Edge o1, Edge o2) {return o1.d - o2.d;}});heap.offer(new Edge(0, 0));while (!heap.isEmpty()) {Edge V = heap.poll();int dist = V.d, t = V.v;// 找未被访问的点if (st[t]) continue;st[t] = true;for (int i = h[t]; ~i != 0; i = ne[i]) {int j = e[i];if (d[j] > d[t] + w[i]) {d[j] = d[t] + w[i];heap.add(new Edge(d[j], j));}}}}public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {n = nextInt();m = nextInt();Arrays.fill(h, -1);while (m-- != 0) {int a = nextInt();int b = nextInt();int c = nextInt();add(a, b, c);add(b, a, c);}k = nextInt();while (k-- != 0) {int x = nextInt();add(0, x, 0);}dijkstra();Q = nextInt();while (Q-- != 0) {y = nextInt();out.println(d[y]);}out.flush();}
}
朴素Dijkstra

分析
朴素Dijkstra算法适用于求稠密图的单源最短路径问题,思想是进行n次迭代,每次从所有的未被访问过的点中找一个距离1号点最近的点,标志它被访问过了,再用该点去更新其他点的最短距离。
代码
#include
#include
using namespace std;const int N = 510;
int g[N][N];
bool vis[N];
int d[N], n, m;int dijkstra()
{memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof d);d[1] = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){int t = -1;for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++){if (!vis[j] && (t == -1 || d[t] > d[j])) t = j;}vis[t] = true;for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)d[j] = min(d[j], d[t] + g[t][j]);}return d[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f ? -1 : d[n];}int main()
{cin >> n >> m;memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof g);while (m--){int x, y, z;cin >> x >> y >> z;//去重边g[x][y] = min(g[x][y], z);}cout << dijkstra() << endl;return 0;
}
堆优化Dijkstra
分析
堆优化Dijkstra算法适用于求稀疏图的单源最短路径问题,与朴素Dijkstra相比,堆优化Dijkstra算法用小根堆维护最短路径,采用优先队列实现,提高寻找最短边的效率。队头元素表示最短路径的距离以及当前的点。用队头元素更新其他点的最短路径。
代码
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;typedef pair PII;const int N = 100010;int h[N], e[N], ne[N], w[N], idx;
int d[N];
bool st[N];
int n, m;void add(int a, int b, int c)
{e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}int dijkstra()
{memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof d);d[1] = 0;priority_queue, greater> heap;//第一关键字为距离, 默认以第一关键字排序heap.push({0, 1});while (heap.size()){auto t = heap.top();heap.pop();int v = t.second;//找未被访问的点if (st[v]) continue;st[v] = true;for (int i = h[v]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){int j = e[i];//更新最短路径if (d[j] > d[v] + w[i]){d[j] = d[v] + w[i];heap.push({d[j], j});}}}return d[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f ? -1 : d[n];}int main()
{scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);memset(h, -1, sizeof h);while (m -- ){int a, b, c;scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);add(a, b, c);}cout << dijkstra() << endl;return 0;
}