文章目录
- 前言
- 问题
- 程序设计
- 几何区域
- 网格单元
- 刚度矩阵组装
- 数值结果
- 问题区域网格
- u 值图像(结果导出借助Matlab画图)
- 总结
前言
本文利用C++语言实现在二维任意区域(内部可有“洞)求解拉普拉斯方程的数值解。可以将区域以及边界信息写在文本文件中, 程序有专门的接口读入数据。
问题
区域

方程
∇2u(x,y)=0inΩ(1)u=uˉ(x,y)onΓu(2)q=∂u∂n⃗=0onΓq(3)\nabla^2u(x, y) = 0 \ \ \ \ in \ \ \Omega \ \ \ (1) \\ u = \bar{u}(x,y) \ \ \ \ on \ \ \ \Gamma_u \ \ \ (2) \\ q = \frac{\partial u}{\partial \vec{n}} = 0 \ \ \ on \ \ \ \Gamma_q \ \ \ (3) \\ ∇2u(x,y)=0 in Ω (1)u=uˉ(x,y) on Γu (2)q=∂n∂u=0 on Γq (3)
程序设计
几何区域
//
// Created by guihun on 2022/10/24.
//#ifndef Geometry_h
#define Geometry_h#include
#include
#include
#include
网格单元
//
// Created by guihun on 2022/10/24.
//#ifndef FEMMesh_h
#define FEMMesh_h#include
#include
#include
#include
刚度矩阵组装
//
// Created by guihun on 2022/10/24.
//
#ifndef _FEM_EQUATION_H_
#define _FEM_EQUATION_H_#include
#include
#include
数值结果
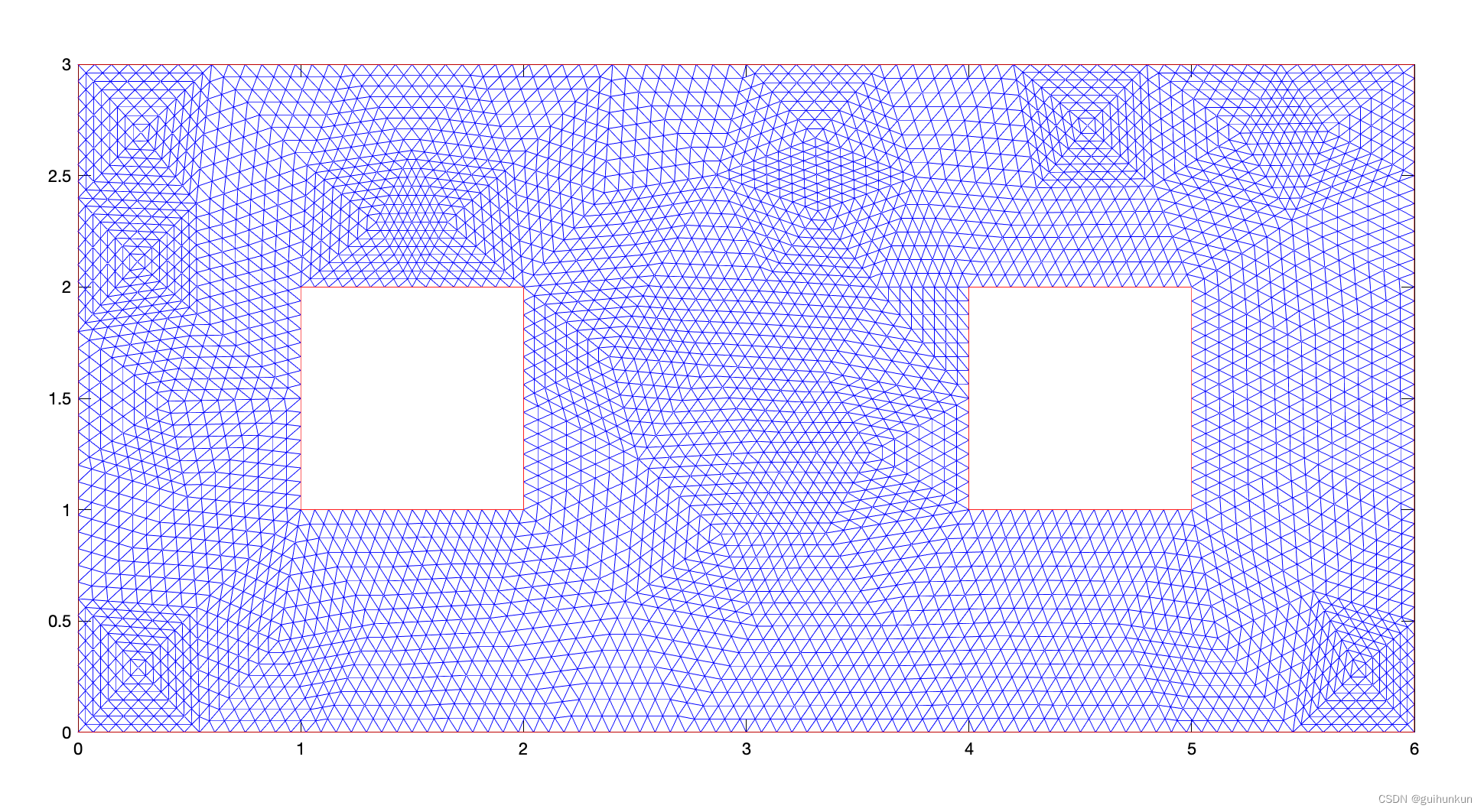
问题区域网格
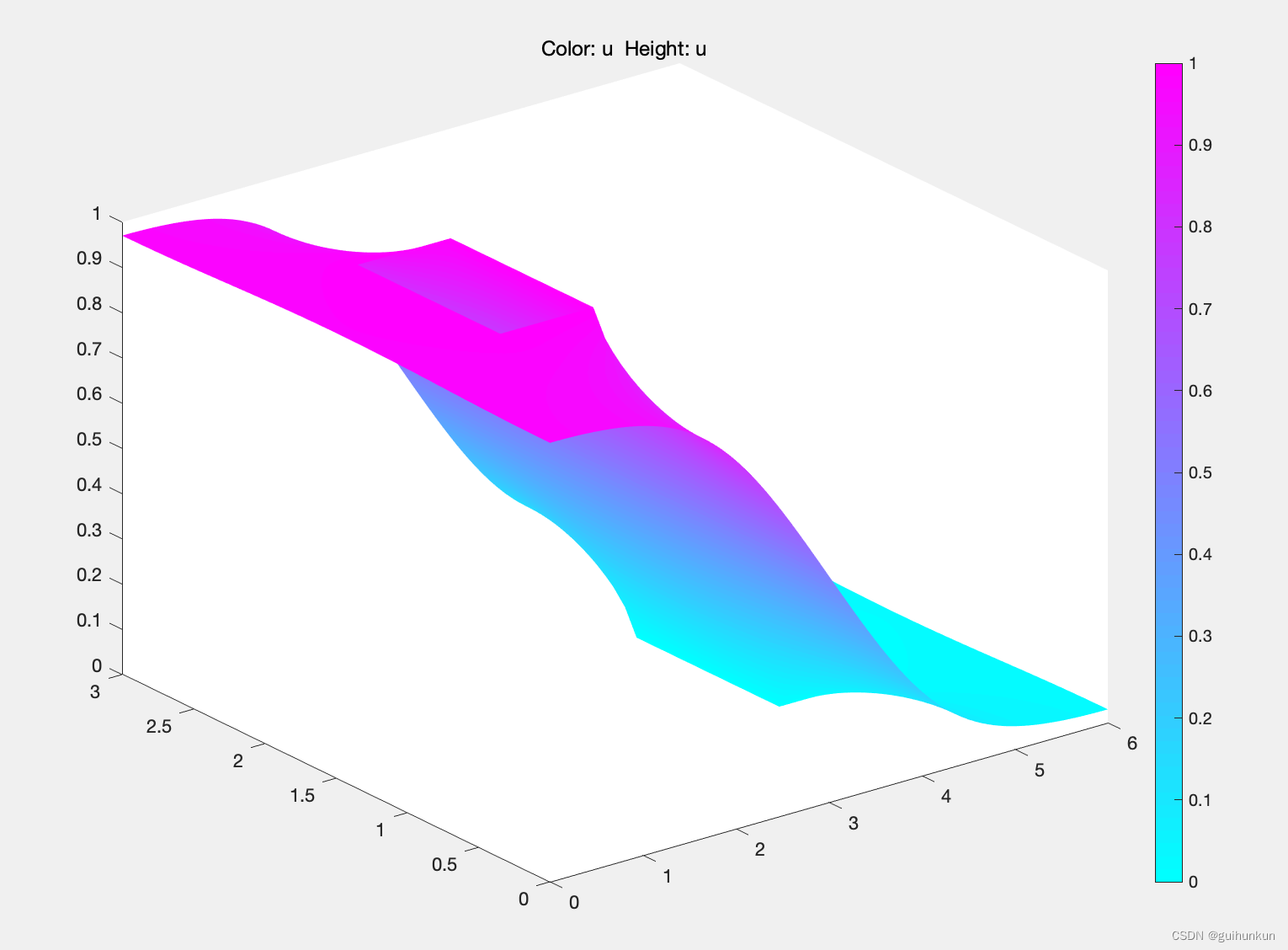
u 值图像(结果导出借助Matlab画图)
总结
利用C++实现可以很好的学习软件设计思路,做各式适合接口(例如将几何区域的信息写入文本文件, 通过程序读取),同时对有限元方法的单刚组总刚有一个更深的理解。本程序借助gmsh的C++接口实现剖网格, 可以参考我的另一篇博客 Gmsh剖二维网格教程附代码 。


