高完整性系统工程(一): Safety Engineering, HAZOP Fault Tree Analysis
目录
1. 因果性不等同于相关性
2. HAZOP
2.1 学习HAZOP
2.2 HAZOP概览
2.3 Assessing Hazard Risks 评估
2.4 示例场景
2.5 HAZOP Guidewords
2.6 HAZOP Process
2.7 HAZOP Outcomes
2.8 HAZOP Summary
3. FAULT TREE ANALYSIS
3.1 Analysis Outcomes
1. 因果性不等同于相关性
因果关系的缺失是由反事实推理。例如,气压计读书总是在暴风雨前下降,但气压计的读数下降不会引起暴风雨。
2. HAZOP
HAZARDS AND OPERABILITY STUDY(危害和可操作性研究)
2.1 学习HAZOP
它是一个初步危险分析的方法
- 探索性分析,系统地集思广益,找出可能出错的地方
- 20世纪50年代,最初是为了了解化学过程中的危险而引入的。
- 由于其有效性,在安全关键型软件工程中被采用
2.2 HAZOP概览
Input:作为 design items 集合的高级系统描述
Design item:一个预期的行为,例如,一个过程中的事件或一个状态转换。例如:当传感器X被触发时,阀门B立即被关闭。
每个设计项目都要系统地进行 mutated(突变),以分析当预期行为没有发生时可能发生的情况,并确定 risk(后果和频率)。
2.3 Assessing Hazard Risks 评估
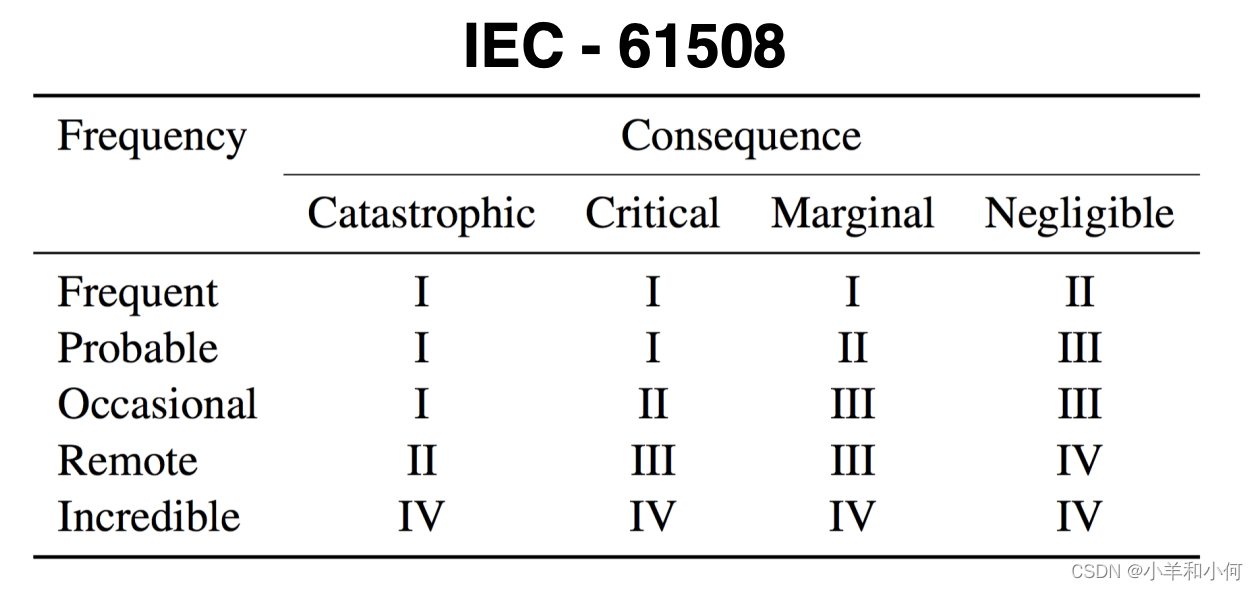
- Class I: Intolerable risk. 不可容忍的风险
- Class II: Undesirable risk and tolerable only if risk reduction is impractical. 不理想的风险,只有在减少风险不切实际的情况下才可以容忍
- Class III: Tolerable risk if the cost of risk reduction would exceed the improvement gained. 可容忍的风险,如果减少风险的成本超过所获得的改善
- Class IV: Negligible risk. 可忽略的风险
2.4 示例场景
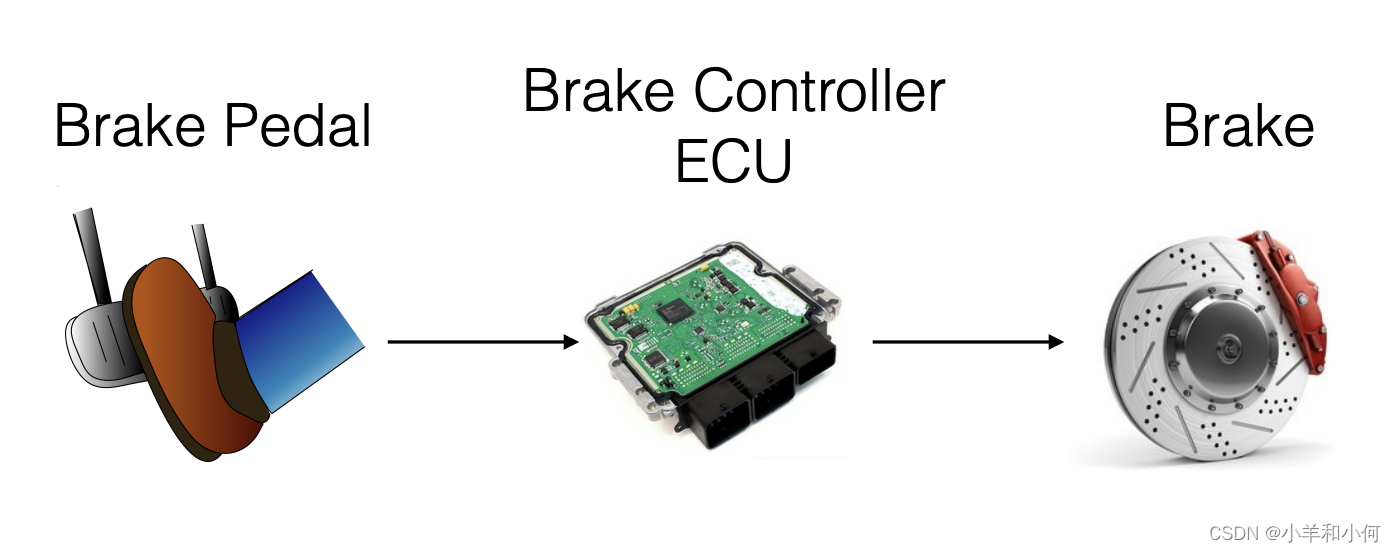
当检测到制动踏板压力迅速增加时,ECU将全力制动,以实施紧急制动。制动控制器的控制回路被安排为每1/10秒运行一次。当脚下压力发生变化时,制动控制器ECU接收来自制动踏板的信号。
Design Item
制动控制器ECU在其脚部压力变化时,接收来自制动踏板的信号
What if there is no signal from the brake pedal?
What if the signal comes early?
What if the signal comes late?
对于每一项,思考可能出现的潜在危险,并对其后果进行评级(catastrophic 灾难性的、critical 关键的、marginal 边缘的、negligible 可忽略的)。
What if there is no signal from the brake pedal?
1. car fails to stop. Consequence: Catastrophic 灾难性的
2. car gets stuck. 汽车卡住 Consequence: Critical 关键的
What if the signal comes early?
1. nonsensical, not applicable 毫无意义,不适用
2. car brakes too quickly 汽车刹车太快
What if the signal comes late?
1. car fails to stop in time. Consequence: Catastrophic 灾难性的
2. car fails to start in time. Consequence: Critical 关键的
2.5 HAZOP Guidewords

2.6 HAZOP Process
对每个 design item 设计项目
对每个 guideword 指导词
对照设计项目 interpret 解释导语(问 "它可能意味着什么"?)
给出与预期行为的 deviations 偏差,确定每个偏差的潜在 causes 原因
潜在的 consequences 后果
为减轻其影响而采取的 safeguards 保障措施
risk 风险
设计 recommendations 建议
2.7 HAZOP Outcomes
大的危害电子表格
大量的文件
有助于建立安全案例
用于分析未来的安全事故(但必须有人手动分析)
具有挑战性、创造性和有趣的过程
通过将建议反馈到设计中来完成,因为设计建议会改变风险等级
2.8 HAZOP Summary
Overall Process
- Identify design items 确定设计项目
- For each, do each guideword 对每个项目,做每个指导词
- causes 原因
- consequences 后果
- safeguards 保障措施
- risk (design) 风险(设计)
- recommendations 建议
3. FAULT TREE ANALYSIS
我的系统设计是否正确地减轻了在 PHA 期间发现的危险(例如 HAZOP)?
在系统设计的背景下,分析危险发生的时间和方式。
是演绎性的,从危险(或导致危险的事件)到它们是如何引起的
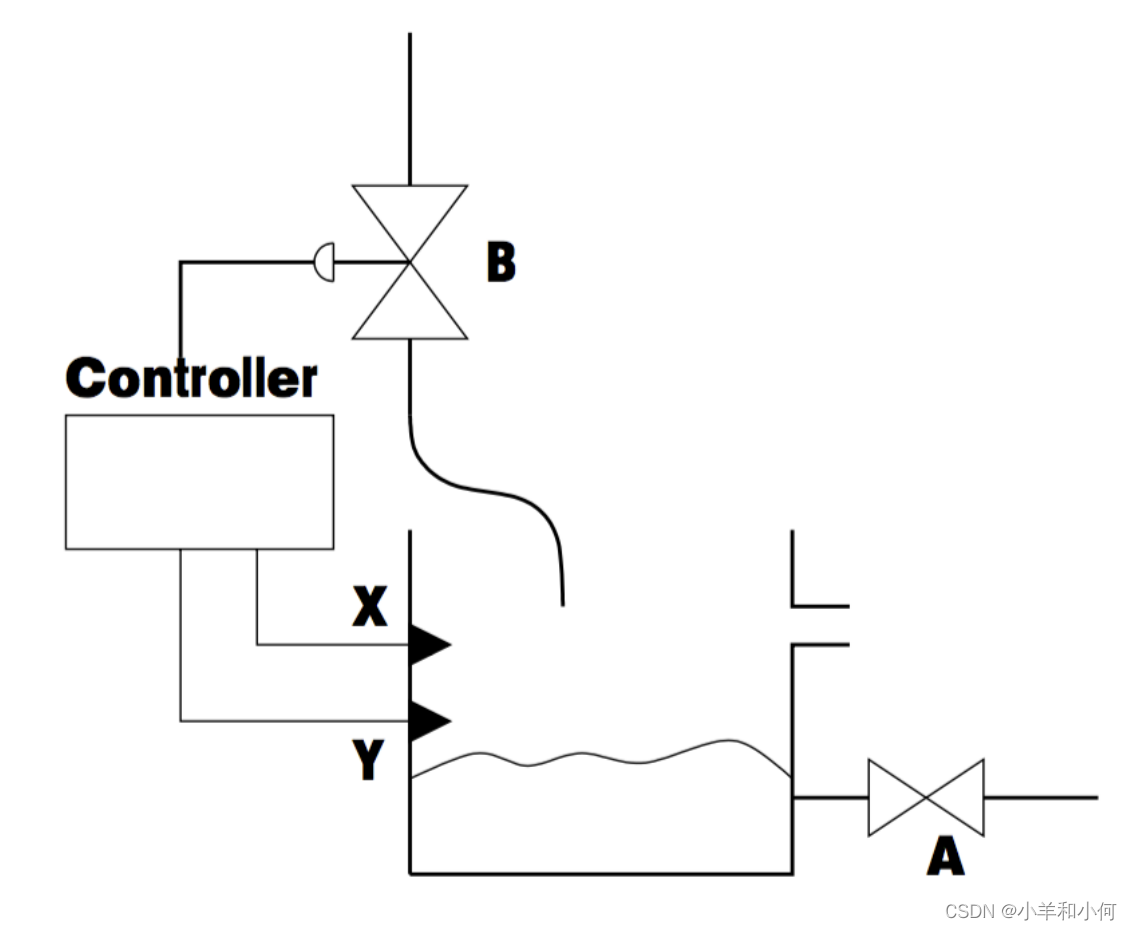




Fault Tree Example
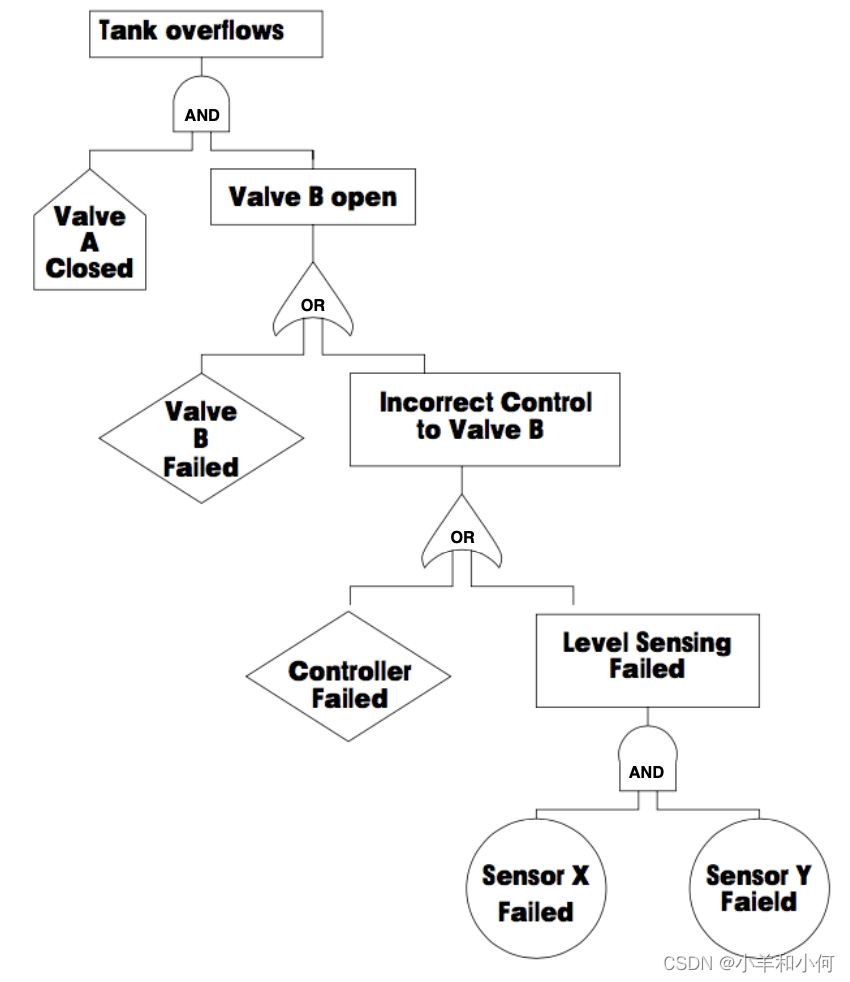
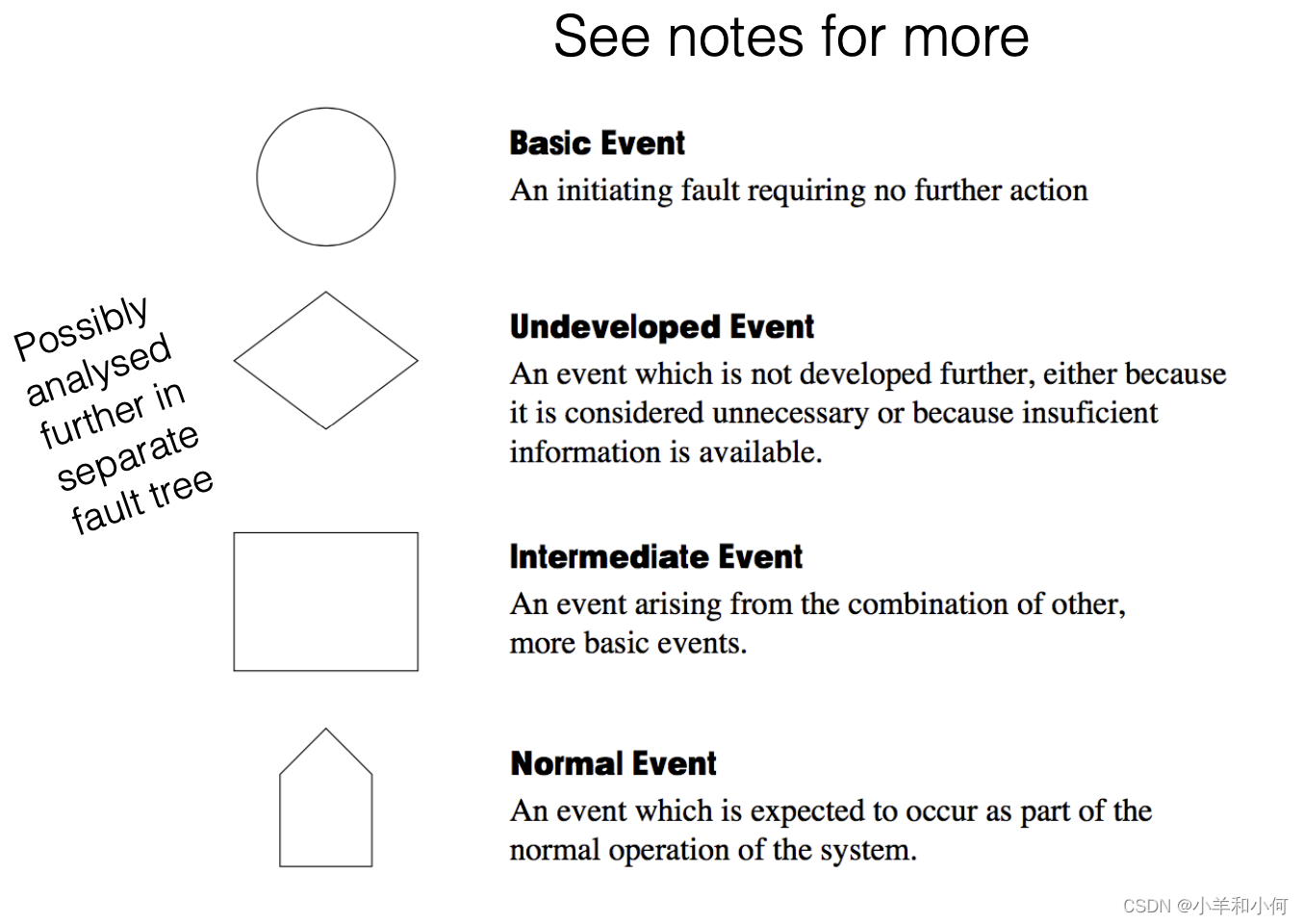
3.1 Analysis Outcomes
危险的成因
故障树分析的应用
决定是否/如何改变设计以防止原因
来确定设计没有防范的原因
安全案例文件允许其他人检查我们的推理
计算发生危险的概率