数据结构---单链表
专栏:数据结构
个人主页:HaiFan.
专栏简介:从零开始,数据结构!!
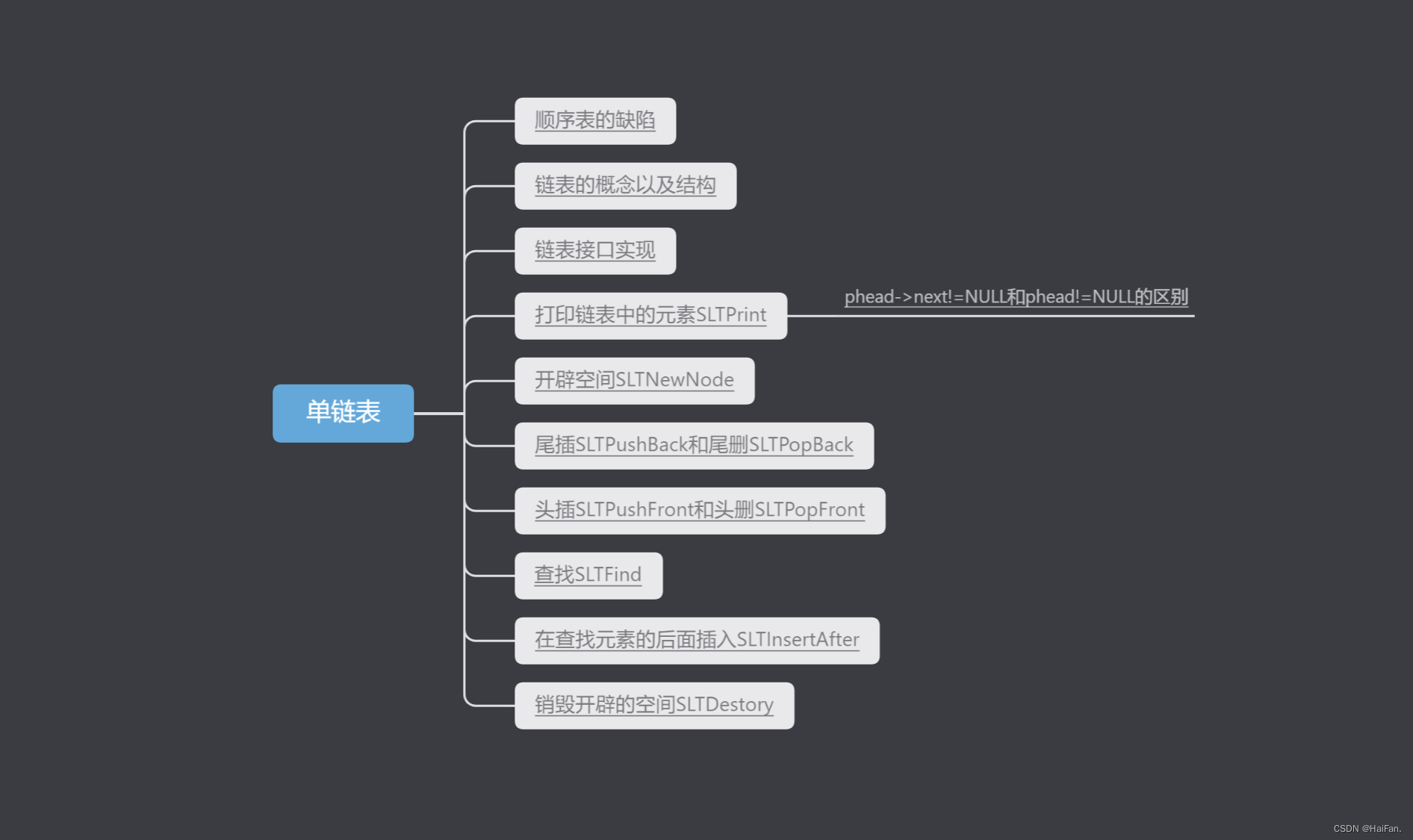
单链表
- 前言
- 顺序表的缺陷
- 链表的概念以及结构
- 链表接口实现
- 打印链表中的元素SLTPrint
- phead->next!=NULL和phead!=NULL的区别
- 开辟空间SLTNewNode
- 尾插SLTPushBack和尾删SLTPopBack
- 头插SLTPushFront和头删SLTPopFront
- 查找SLTFind
- 在查找元素的后面插入SLTInsertAfter
- 在查找元素的后面删除SLTEraseAfter
- 销毁开辟的空间SLTDestory
- 各个接口测试
- 源代码
- 链表和顺序表的区别
前言
顺序表的缺陷
顺序表每一次扩容,都是连续的空间,支持通过下标去访问数据。
但是顺序表的头插,头删,中间删元素,需要把后面的数据覆盖前面的元素,也就是挪动元素,这就导致效率非常的低
并且,顺序表在扩容之后,可能会有一部分空间没有用,这就导致了空间浪费。
链表的概念以及结构
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的 。
链表的结点一般是在堆上申请出来的,从堆上申请的空间,是按照一定策略来分配的,两次申请的空间可能连续,也可能不连续。
链表是每用一块空间,便开辟一块空间,因此,不会造成空间浪费。
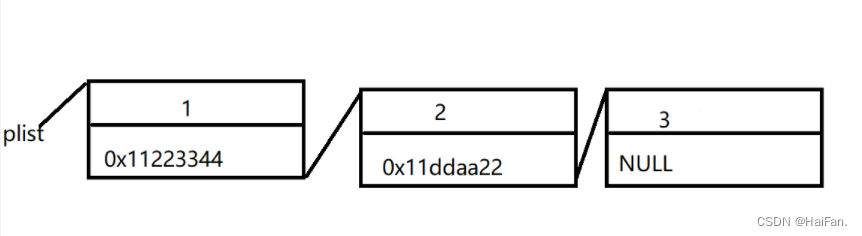
这个图什么意思呢?
把开辟的空间当作2个合在一起的小方块,一个小方块用来存元素的值,一个方块用来存放下一个空间的地址。
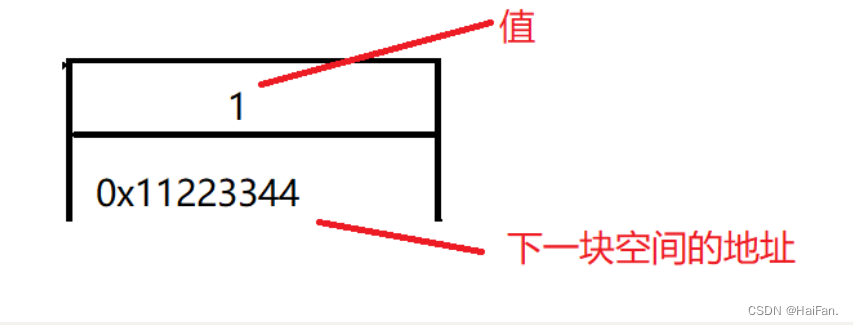
当这个1就是最后一个元素的时候,这个下一块空间的地址就是NULL,因为1后面没有元素了,不能让这个地址乱指向其他的空间。
链表接口实现
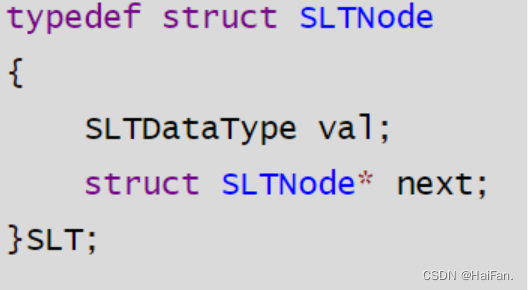
这里,在结构体中要用结构体指针,指针就是地址,这个地址就是用来存放下一个空间的地址的。
typedef int SLTDataType;typedef struct SLTNode
{SLTDataType val;struct SLTNode* next;
}SLT;void SLTPrint(SLT* phead);//打印单链表中的数据SLT* SLTNewNode(SLTDataType x);//每要插入数据,就需要开一一块空间void SLTPushBack(SLT** pphead, SLTDataType x);//尾插
void SLTPopBack(SLT** pphead);//尾删void SLTPushFront(SLT** pphead, SLTDataType x);//头插
void SLTPopFront(SLT** pphead);//头删SLT* SLTFind(SLT** pphead, SLTDataType x);//查找
//单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void SLTInsertAfter(SLT* pos, SLTDataType x);//插入
//单链表在pos位置之后删除元素
void SLTEraseAfter(SLT* pos);//删除void SLTDestory(SLT** pphead);//销毁空间
打印链表中的元素SLTPrint
打印链表中的元素是最容易实现的一个接口。
void SLTPrint(SLT* phead)
{while (phead != NULL){cout << phead->val << "->";phead = phead->next;}cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
这里用一级指针,因为打印链表不会更改链表中的一些东西。
每打印出一个元素,都让phead指向下一块空间,直到走到为NULL的时候为止
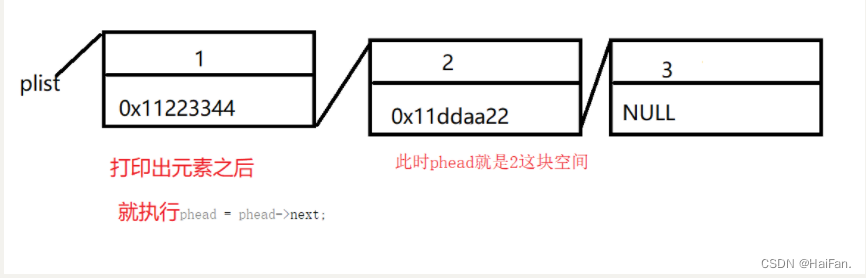
phead->next!=NULL和phead!=NULL的区别
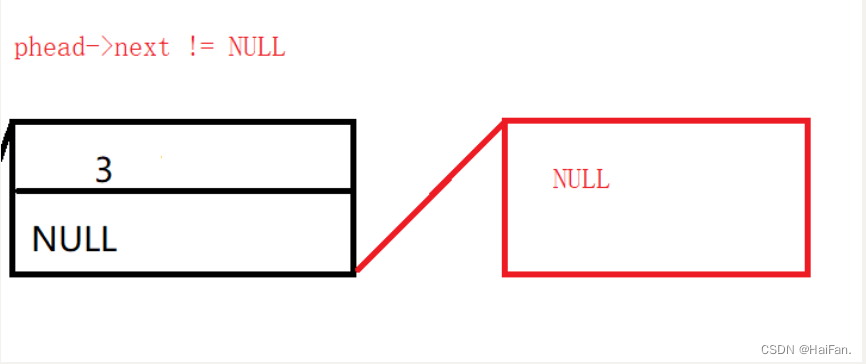
假如现在phead是在3这块空间,那么phead->next就是指向下一块空间,因为下一块空间是NULL,所以,当你写出phead->next != NULL的时候,就会在3这里停止后面的打印。
phead !=NULL是当phead走到NULL的时候才会执行。
开辟空间SLTNewNode
链表是每用一块空间就开辟一块空间。这样不会造成空间浪费。
SLT* SLTNewNode(SLTDataType x)
{SLT* newnode = (SLT*)malloc(sizeof(SLT));newnode->next = NULL;newnode->val = x;return newnode;
}
开辟了空间之后,不要忘记把newnode->next置为NULL,不然就成为野指针了。最后把这块空间返回即可。
尾插SLTPushBack和尾删SLTPopBack
尾插的时候,先调用一下开辟空间的函数,再把开辟的空间返回,用一个结构体指针变量接收。
- 当链表为空的时候,newnode就可以当作链表中的第一块空间。
- 当链表不为空的时候,就需要先找到链表的尾部,然后把newnode链接在链表中即可
void SLTPushBack(SLT** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{SLT* newnode = SLTNewNode(x);if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{SLT* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}
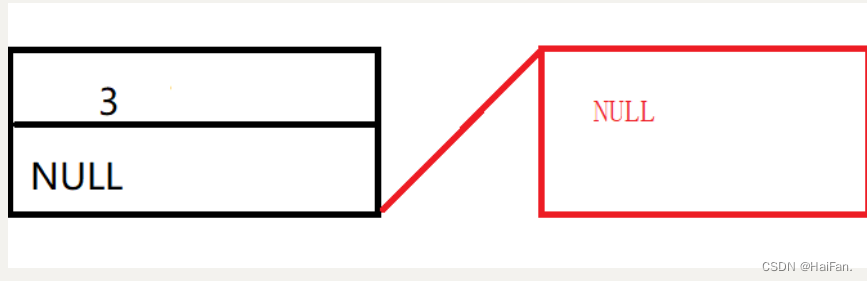
要用一个临时变量走向链表最后一个元素的位置,如果不用临时变量,直接用头元素走到最后一个位置,那么,在打印元素的时候,也是从最后一个元素的位置开始打印的,前面的元素不会打印,因为我们是用指针接收的头元素的位置,通过指针直接去访问内容,指针走到最后就会导致,原本应该指向头元素的指针,就指向了最后的元素。
所以在这里用 tail->next != NULL
尾删分两种情况,当链表中只有一个元素的时候和链表中有n个元素的时候。
第一种情况好说,直接把第一个元素的空间给free掉,在置为空即可。
第二种情况就是先找到尾,但是,在找到尾部之后,不能直接把尾部free掉,而是要先知道倒数第二个元素的位置。
void SLTPopBack(SLT** pphead)
{assert(*pphead);if ((*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else{SLT* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next->next != NULL){ tail = tail->next;}free(tail->next);tail->next = NULL;}
}/*SLTNode* prev = NULL;SLTNode* tail = phead;while (tail->next){prev = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);prev->next = NULL;*/
这两种方法都可以。
头插SLTPushFront和头删SLTPopFront
头插特别容易,先开辟一块空间,然后把这块空间指向头元素空间。在把头元素空间指向新开辟的空间即可。

void SLTPushFront(SLT** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{SLT* newnode = SLTNewNode(x);newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;
}头删之前,要先判断链表中有没有元素,没有元素直接断言。
有一个元素,直接free。
多个元素,先用一个临时变量记录一下头元素指向的下一个元素的地址,然后把头元素给free掉,再让头元素=临时变量。
void SLTPopFront(SLT** pphead)
{assert(*pphead);if ((*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else{SLT* head = (*pphead)->next;free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;*pphead = head;}
}
查找SLTFind
查找元素的时候,把该空间的地址给返回即可,遍历一遍链表即可实现。
SLT* SLTFind(SLT** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{SLT* tail = *pphead;while (tail != NULL){if (tail->val == x){return tail;}tail = tail->next;}return NULL;//没有找到
}
在查找元素的后面插入SLTInsertAfter
先通过SLTFind,找到要插入的位置,然后通过断言来判断这个位置是否合法。
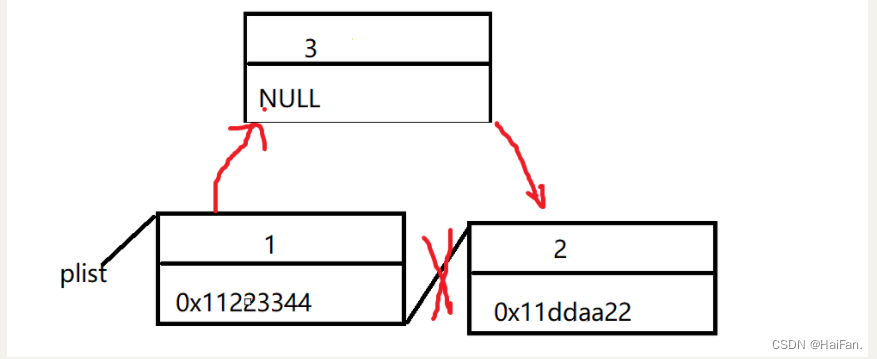
比如要把3插入到1和2之间,把3->next = 1->next,再把1->next = 3就能完成插入。
void SLTInsertAfter(SLT* pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pos);SLT* newnode = SLTNewNode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;}在查找元素的后面删除SLTEraseAfter
还是先断言,判断位置是否合法。

电脑上的画图实在是用不来,原谅我------。。。
void SLTEraseAfter(SLT* pos)
{assert(pos);if (pos->next == NULL){return;}SLT* newnode = pos->next;pos->next = newnode->next;free(newnode);newnode = NULL;
}
销毁开辟的空间SLTDestory
因为空间不一定是连续的,所以需要遍历链表,一个一个的释放
void SLTDestory(SLT** pphead)
{SLT* cur = *pphead;while (cur){SLT* hh = cur->next;free(cur);cur = hh;}
}
各个接口测试
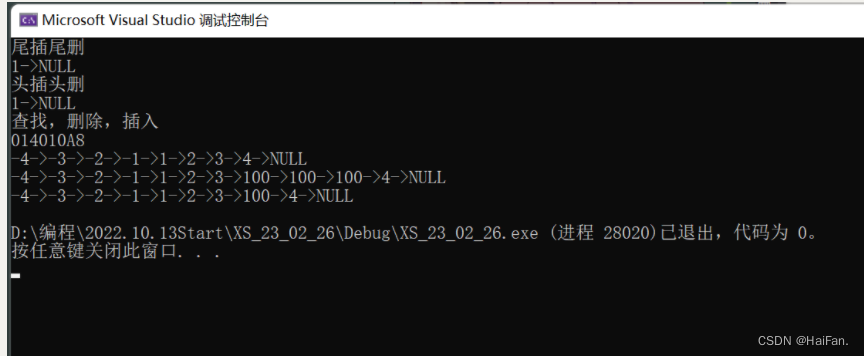
void TestSLTNode()
{SLT* plist = NULL;cout << "尾插尾删" << endl;SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);
}void TestSLTNode1()
{SLT* plist = NULL;cout << "头插头删" << endl;SLTPushFront(&plist, 1);SLTPushFront(&plist, 2);SLTPushFront(&plist, 3);SLTPushFront(&plist, 4);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);
}void TestSLTNode2()
{SLT* plist = NULL;cout << "查找,删除,插入" << endl;SLTPushFront(&plist, -1);SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);SLTPushFront(&plist, -2);SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);SLTPushFront(&plist, -3);SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);SLTPushFront(&plist, -4);SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);SLT* ret = SLTFind(&plist, 3);if (ret){cout << ret << endl;}SLTPrint(plist);SLTInsertAfter(ret, 100);SLTInsertAfter(ret, 100);SLTInsertAfter(ret, 100);SLTPrint(plist);SLTEraseAfter(ret);SLTEraseAfter(ret);SLTPrint(plist);SLTDestory(&plist);
}int main()
{TestSLTNode();TestSLTNode1();TestSLTNode2();return 0;
}
源代码
.h文件
#pragma once#include
#include
#include using namespace std;typedef int SLTDataType;typedef struct SLTNode
{SLTDataType val;struct SLTNode* next;
}SLT;void SLTPrint(SLT* phead);//打印单链表中的数据SLT* SLTNewNode(SLTDataType x);//每要插入数据,就需要开一一块空间void SLTPushBack(SLT** pphead, SLTDataType x);//尾插
void SLTPopBack(SLT** pphead);//尾删void SLTPushFront(SLT** pphead, SLTDataType x);//头插
void SLTPopFront(SLT** pphead);//头删SLT* SLTFind(SLT** pphead, SLTDataType x);//查找
//单链表在pos位置之后插入x
void SLTInsertAfter(SLT* pos, SLTDataType x);//插入
//单链表在pos位置之后删除元素
void SLTEraseAfter(SLT* pos);//删除void SLTDestory(SLT** pphead);//销毁空间
.cpp文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "SList.h"void SLTPrint(SLT* phead)
{while (phead){cout << phead->val << "->";phead = phead->next;}cout << "NULL" << endl;
}SLT* SLTNewNode(SLTDataType x)
{SLT* newnode = (SLT*)malloc(sizeof(SLT));newnode->next = NULL;newnode->val = x;return newnode;
}void SLTPushBack(SLT** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{SLT* newnode = SLTNewNode(x);if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{SLT* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}void SLTPopBack(SLT** pphead)
{assert(*pphead);if ((*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else{SLT* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next->next != NULL){ tail = tail->next;}free(tail->next);tail->next = NULL;}
}void SLTPushFront(SLT** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{SLT* newnode = SLTNewNode(x);newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;
}void SLTPopFront(SLT** pphead)
{assert(*pphead);if ((*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else{SLT* head = (*pphead)->next;free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;*pphead = head;}
}SLT* SLTFind(SLT** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{SLT* tail = *pphead;while (tail != NULL){if (tail->val == x){return tail;}tail = tail->next;}return NULL;//没有找到
}void SLTInsertAfter(SLT* pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pos);SLT* newnode = SLTNewNode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;}void SLTEraseAfter(SLT* pos)
{assert(pos);if (pos->next == NULL){return;}SLT* newnode = pos->next;pos->next = newnode->next;free(newnode);newnode = NULL;
}void SLTDestory(SLT** pphead)
{SLT* cur = *pphead;while (cur){SLT* hh = cur->next;free(cur);cur = hh;}
}
test.cpp文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "SList.h"void TestSLTNode()
{SLT* plist = NULL;cout << "尾插尾删" << endl;SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);
}void TestSLTNode1()
{SLT* plist = NULL;cout << "头插头删" << endl;SLTPushFront(&plist, 1);SLTPushFront(&plist, 2);SLTPushFront(&plist, 3);SLTPushFront(&plist, 4);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);
}void TestSLTNode2()
{SLT* plist = NULL;cout << "查找,删除,插入" << endl;SLTPushFront(&plist, -1);SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);SLTPushFront(&plist, -2);SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);SLTPushFront(&plist, -3);SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);SLTPushFront(&plist, -4);SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);SLT* ret = SLTFind(&plist, 3);if (ret){cout << ret << endl;}SLTPrint(plist);SLTInsertAfter(ret, 100);SLTInsertAfter(ret, 100);SLTInsertAfter(ret, 100);SLTPrint(plist);SLTEraseAfter(ret);SLTEraseAfter(ret);SLTPrint(plist);SLTDestory(&plist);
}int main()
{TestSLTNode();TestSLTNode1();TestSLTNode2();return 0;
}
链表和顺序表的区别
| 不同点 | 顺序表 | 链表 |
|---|---|---|
| 存储空间上 | 物理上一定连续 | 逻辑上连续,但物理上不一定 连续 |
| 随机访问 | 支持O(1) | 不支持:O(N) |
| 任意位置插入或者删除 元素 | 可能需要搬移元素,效率低 O(N) | 只需修改指针指向 |
| 插入 | 动态顺序表,空间不够时需要 扩容 | 没有容量的概念 |
| 应用场景 | 元素高效存储+频繁访问 | 任意位置插入和删除频繁 |
| 缓存利用率 | 高 | 低 |