BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目
BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目
1.BoostSearcher这个项目是什么?
答:一个为Boost文档建立索引的站内搜索引擎,简单的说就是一个类似于csdn站内文档搜索框。
项目展示:
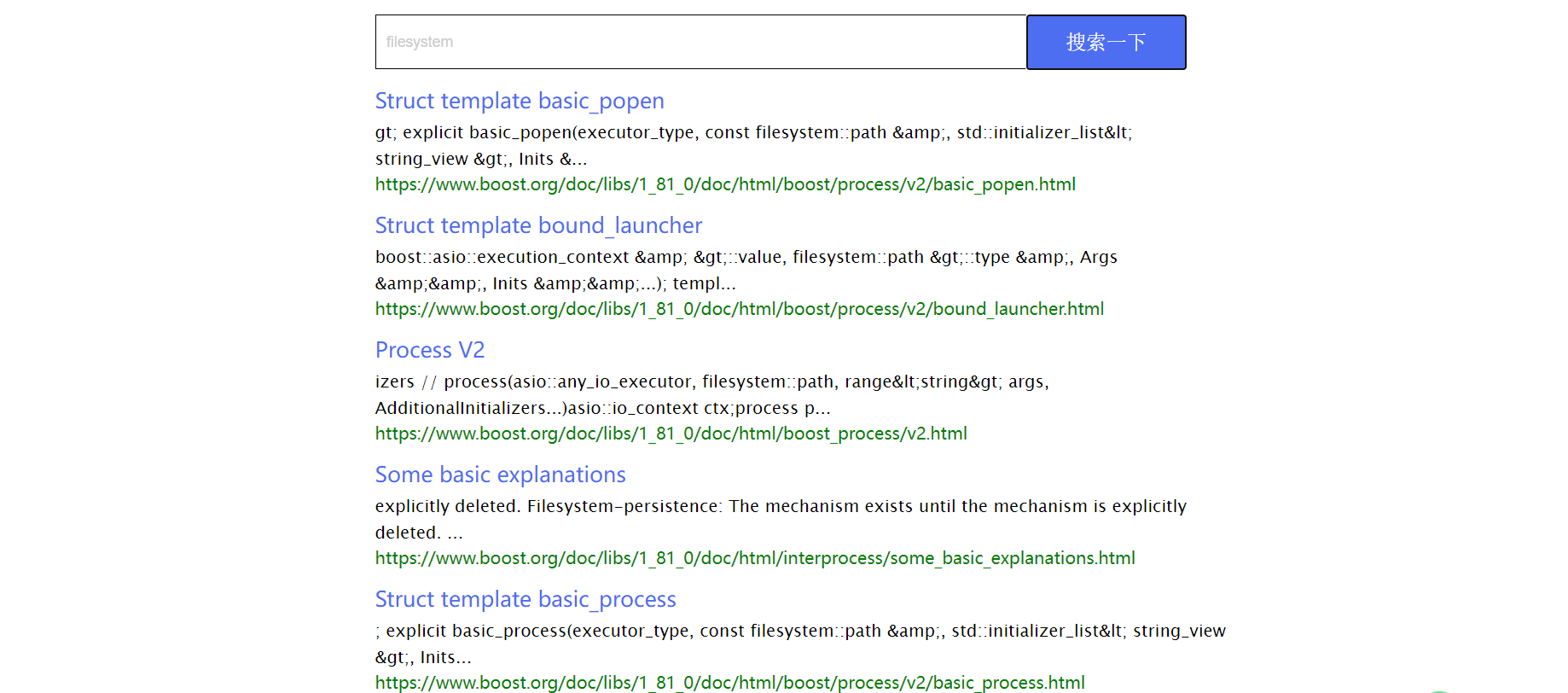
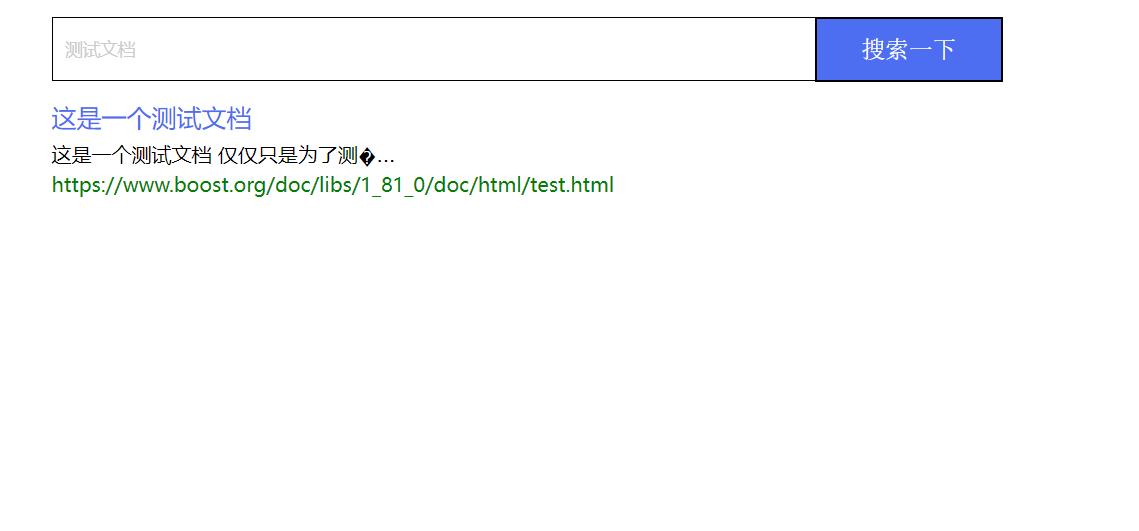
gitee:https://gitee.com/zxlfx/boost-search-engine-project
2.为什么做BoostSearcher?
答:学习和了解搜索引擎的底层原理,虽然无法做出一个像百度、360搜索这样的全网搜索引擎,但可以从中窥探出搜索引擎所具备的一些宏观设计。
3.怎么做BoostSearcher?
答:我分为以下几个步骤完成BoostSearcher项目:
- 了解BoostSearcher宏观原理。
- 获取数据源(html网页)
- 对数据建立正排、倒排索引(核心)
- 编写html服务,为前端提供服务。
- 日志的补充及项目的扩展。
4.项目设计的技术
前端:HTML5、CSS、JS、jQuery、Ajax(不需要了解太多,该项目主要是后端编写,不写前端也行)
后端:C/C++、C++11,STL库、标准库Boost(主要文件库)、jsoncpp(序列化和反序列化)、cppjieba(分词工具)、cpphttp-lib(提供http服务)
5.介绍宏观原理
宏观图:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ZaCyru4b-1677284957534)(BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目.assets/image-20230223192434446.png)]](/uploadfile/202405/73d593f3ae15a7e.png)
宏观图解释:
-
做法是先获取数据源(html网页),如何获取?
答:从Boost官网下载文档HTML网页。
-
对HTML网页进行解析和提取,如何解析和提取?
答:解析网页HTML,提取出title、摘要、url。组成一个个结构体,构成关键字的查找依据。
-
建立正排和倒排索引?什么是正排索引?什么是倒排索引?
答:正排索引如下(文档id和正排文档的映射关系)。
文档id 正排文档(DocInfo) 1 正排文档1 2 正排文档2 3 正排文档3 4 正排文档4 倒排索引如下(关键字和倒排拉链的映射关系):
关键字 倒排拉链(Inverted_List) 我 倒排文档1、倒排文档2、倒排文档3 不吃 倒排文档2 香菜 倒排文档1、倒排文档3 struct DocInfo//正排文档 {int id;//文档id,这个作用后续会解答。std::string title;//文档标题std::string content;//文档内容,这里的内容指的是全html文本去掉标签后的字符串,如:你好去掉之后就是"你好”std::string url;//文档url }struct Inverted_ele//倒排文档 {int id;//文档iddouble weight;//关键字在该文档的权重std::string word;//关键字,这个作用后续会解答 }typedef std::vectorInverted_List;//倒排拉链 如果我们需要查找这样的一句话:
我必须全力守卫我的祖国。根据分词工具分解成以下关键字:“我”、“必须”、“全”、“力”、“全力”、“守卫”、“我的祖国”、“我的”、“祖国”。
具体分解成什么样的关键字,我们不需要关心,这是分词工具做的事情,本项目只使用分词工具,不设计原理细节。
接下来,只需要把这些关键字对应的倒排拉链(Inverted_List)全部组合到一起,组合方式:相同的倒排文档权重相加,然后放到一个新的Inverted_List中。并进行权重降序排序,然后就可以通过倒排文档(Inverted_ele)找到对应的正排文档(DocInfo),即找到一个个(title、content、url),然后将一个个正排文档序列化组成字符串返回给客户端。 注:序列化:将结构体数据转化为字符串。
6、项目编写
6.1 获取数据源
-
第一步:从Boost官网下载文档网页集合,然后用rz命令上传至服务器。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-uuQfoSW6-1677284957534)(BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目.assets/image-20230223195604905.png)]](/uploadfile/202405/a15e9ed7e77c82a.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-MtIauYA7-1677284957535)(BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目.assets/image-20230223195649646.png)]](/uploadfile/202405/ad0b32b1cb0a73e.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-q0D5YVAo-1677284957535)(BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目.assets/image-20230223202934406.png)]](/uploadfile/202405/8727fb93f08c.png)
![ [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-vdZ5cb84-1677284957536)(BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目.assets/image-20230223203253802.png)]](/uploadfile/202405/121c907f5d7b04e.png)
我们只需要html中的.html文件,其他的不需要。
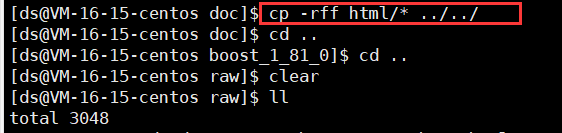
将html目录下的所有文件拷贝到raw目录下。
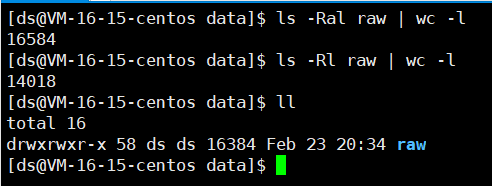
提取raw下的所有HTML文件为一个个DocInfo结构体,用\3分割:title\3content\3url,再用\n分割DocInfo结构体,最后组成一个大文本文件。
struct DocInfo
{std::srting title;std::string content;std::string url;
}
大文本文件内容简述:title\3content\3url \n title\3content\3url \n …(这里我用二进制写文件,不用二进制写文件也行)
编写解析代码:parser.cc
***第一步搭建框架***
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include"util.hpp"const std::string src_path = "./data/input";//源目录
const std::string raw_path = "./data/raw/raw.txt";//解析源目录下的所有.html文件,组成一个raw.txt大文本文件typedef struct DocInfo{std::string title;//标题std::string content;//内容std::string url;//url
}DocInfo_t;int main()
{std::vector filenames;std::vector results;//将src_path目录下的所有.html普通文件全部列举到filenames容器中if(!EnumFile(src_path,filenames)){std::cerr<<"EnumFile() error"< 接下来只需要完成EnumFile()、ParseHtml()、SaveHtml()函数的编写
-
EnumFIle()函数由于C++的文件操作不适应递归遍历目录文件,因此我选择使用Boost文件系统库。
安装boost库命令:sudo yum install -y boost-devel
如何使用Boost文件系统库呢?
这里只对用到的函数代码做解释,具体学习还需要到Boost官网看文档学习。
bool EnumFile(const std::string& src_path,std::vector& filenames)
{namespace fs = boost::filesystem;//引用命名空间。fs::path root_path(src_path);//定义path变量,用src_path初始化。if(!fs::exists(root_path))//判断root_path目录是否存在,即判断src_path目录是否存在。{std::cerr<path().extension() != ".html")//判断普通文件的后缀是不是.html。{continue;//后缀不满足,判断下一个。}//得到了一个带路径的html普通文件。filenames.push_back(iter->path().string());}return true;
}
2.ParseHtml()函数
该函数的作用是:读取一个个带路径的html文件,然后解析提取为一个个DocInfo结构体保存到results容器中(vector)。
ParseHtml()函数基本框架:
bool ParseHtml(const std::vector& filenames,std::vector& results)
{for(std::string file:filenames)//遍历读取带路径的html文件名{std::string result;//读取html文件内容到result中if(!ns_util::FileUtil::ReadFile(file,&result))//由于可能多个地方需要读取文件,于是将ReadFile写到了一个工具类{continue;}DocInfo_t doc;//提取html文件的内容到doc结构体中if(!ParseTitle(result,&doc.title))//提取标题,需要的是result。{continue;}if(!ParseContent(result,&doc.content))//提取内容,需要的是result。{continue;}if(!ParseUrl(file,&doc.url))//提取url,需要的是html文件路径名。{continue;}results.push_back(std::move(doc));//doc插入到results容器中,使用move调用移动赋值,减少拷贝。}return true;
}
util.hpp中ReadFIle()的编写
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#includenamespace ns_util
{namespace FileUtil{static bool ReadFile(const std::string file,std::string* result){std::ifstream ifs(file,std::ios::in);if(!ifs.is_open()){std::cerr<<"file open error"< 接下来依次完成ParseTitle()、ParseContent()、ParseUrl()编写。
ParseTitle():提取标题
static bool ParseTitle(const std::string& result,std::string* title)
{//比如解析:你是个好人 std::size_t begin = result.find("");if(begin == std::string::npos){return false;}begin += std::string("<title>").size();std::size_t end = result.find(" ");if(end == std::string::npos){return false;}if(begin > end){return false;}*title = result.substr(begin,end-begin);return true;
}
ParseContent():提取内容
static bool ParseContent(const std::string& result,std::string* content)
{//简易的状态机,读一读代码很好理解enum status{LABLE,CONTENT };status s = LABLE;for(char c : result){switch(s){case LABLE:if(c == '>')s = CONTENT;break;case CONTENT:if(c == '<')s = LABLE;else {if(c == '\n')//这里我把html文本中的所有'\n'全部替换成了' ',就是为了用getline后面读取一个个DocInfo结构体方便,所以需要替换掉'\n',选择' '可以,选择'\4'可以。但'\3'不行,会和DocInfo成员变量的SEP分隔符冲突。c = ' ';*content += c;} break;default:break;}}return true;
}
ParseUrl():提取Url
static bool ParseUrl(const std::string& file,std::string* url)
{std::string url_head = "https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_81_0/doc/html";//官方的文档访问路径std::string url_end = file.substr(src_path.size());//因为file是带路径的文件名,需要把它前面的本地路径去掉,换上官网的路径。*url = url_head + url_end;return true;//注:搜索引擎不存储站点网站,只是将搜索结果的url返回,告诉你该访问哪个网站。
}
SaveHtml()函数:保存results的内容为一个大文本文件。
bool SaveHtml(const std::vector& results,const std::string raw_path)
{
#define SEP '\3'//DocInfo成员函数分隔符,如:title\3content\3urlstd::ofstream ofs(raw_path,std::ios::out | std::ios::binary);//二进制写打开文件if(!ofs.is_open()){std::cerr< 至此,完成了一个文件的清洗,最后得到了一个包含若干个DocInfo字符串的大文本文件。
6.2 建立正排和倒排索引
本项目终于迎来了它的核心部分:正排索引和倒排索引
第一步:建立正排索引
我们前面简述过了一遍正排索引的原理,这里我再次分析一遍。
| 文档id | 文档(DocInfo) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 文档1 |
| 2 | 文档2 |
| 3 | 文档3 |
| 4 | 文档4 |
正排索引即文档id与文档DocInfo的映射关系,这里的DocInfo结构体为:
struct DocInfo//正排文档
{int id;//文档id,这个作用后续会解答。std::string title;//文档标题std::string content;//文档内容,这里的内容指的是全html文本去掉标签后的字符串,如:你好去掉之后就是"你好”std::string url;//文档url
}
注意与parser.cc里面的DocInfo结构体区分,这里多了一个id,作用会后续解答。
倒排索引即关键字与倒排拉链的映射关系。
什么是关键字?
如果一句话为:”我不吃香菜“
那么关键字可以为:“我”、“不吃”、“香菜”(具体取决于分词工具)
| 关键字 | 倒排拉链(Inverted_List) |
|---|---|
| 我 | 倒排文档1、倒排文档2、倒排文档3 |
| 不吃 | 倒排文档2 |
| 香菜 | 倒排文档1、倒排文档3 |
倒排拉链是什么?
struct Inverted_ele//倒排文档
{int id;//文档iddouble weight;//关键字在该文档的权重std::string word;//关键字,这个作用后续会解答
}typedef std::vector Inverted_List;//我称它为倒排拉链
倒排拉链即 std::vector
如果用户搜索“我不吃”,那么分词工具大概率分为:“我”、“不吃”。
然后查找倒排索引,找到各个关键字对应的倒排拉链,就是:
(倒排文档1、倒排文档2、倒排文档3)
(倒排文档2)
再合并成一个新的倒排拉链(倒排文档1、倒排文档2、倒排文档3),相同的倒排文档权重需要相加,因为倒排文档2中既有关键字“我”也有“不吃”,权重需要相加。
然后通过倒排文档中的id查正排索引,找到对应的正排文档(正排文档1、正排文档2、正排文档3)。
然后将各个正排文档由结构体转化为字符串组合成一个Json字符串返回(由于内存对齐等平台原因,网络上直接发送结构体二进制数据容易出错。),这里需要用序列化与反序列化工具:Json、Xml、Protobuf,我选择的是Json。
说了这么多了,现在开始完成索引的建立
索引框架的编写:
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include"util.hpp"
#includenamespace ns_index
{struct ForwardElem//正排文档{std::string title;//标题std::string content;//内容std::string url;//urluint64_t id;//正排文档id};struct InvertedElem//倒排文档{uint64_t id;//正排文档idint weight;//文档权重std::string word;//关键字};typedef std::vector InvertedList;//倒排拉链class Index{private:std::vector forward_index;//正排索引std::unordered_map inverted_index;//倒排索引public:Index(){};~Index(){};public:ForwardElem* GetForwardIndex(uint64_t id)//根据文档id获取正排文档,函数1{}InvertedList* GetInveredList(std::string& word)//根据关键字获取倒排拉链,函数2{}bool BuildIndex(const std::string& raw_path)//根据parser.cc得到的大文本文件,建立正排和倒排索引,函数3{}private:ForwardElem* BuildForwardIndex(const std::string& line)//建立正排索引,函数4{}bool BuildInvertedIndex(const ForwardElem& fe)//建立倒排索引,函数5{}};
}
现在剩下的是我们需要完成对上面五个函数代码编写。
先来GetForwardIndex()函数:通过文档id获取正排文档
ForwardElem* GetForwardIndex(uint64_t id){if(id > forward_index.size())//防止越界{std::cerr<<"id index beyond range"<编写GetInveredList()函数:通过关键字获取倒排拉链
InvertedList* GetInveredList(std::string& word)
{auto iter = inverted_index.find(word);//查找关键字是否被建立倒排索引,iter类型为pairif(iter == inverted_index.end())//关键字不在倒排索引内{std::cerr<<"this word not exists invertedlist"<second;//返回倒排拉链
}
接下来写BuildIndex()函数:建立索引(正排索引和倒排索引)
bool BuildIndex(const std::string& raw_path)//parser.cc处理后保存的大文本文件的路径
{std::ifstream ifs(raw_path,std::ios::in | std::ios::binary);//保存文件时是按照二进制方式的if(!ifs.is_open()){std::cerr<最后完成BuildForwardIndex()函数和BuildInvertedIndex()函数就大功告成了。
先BuildForwardIndex()函数
BuildForwardIndex函数的主要目的是将title\3content\3url这样的字符串转化为DocInfo这样的结构体,所以需要采用字符串截取操作,可以使用find()+ substr(),但比较麻烦。不推荐使用strtok,因为它会改变原始字符串。这里我选择使用Boost库中的split函数。
我把split函数写到工具类(utill.hpp)中:
namespace StringUtil
{static void Split(const std::string line,std::vector* result,const std::string& sep){boost::split(*result,line,boost::is_any_of(sep),boost::token_compress_on);}
}
这里的split第三个参数是处理特殊情况:比如title\3\3\3\3\3\3content\3url
如果写为boost::token_compress_off分隔结果中会有多个空串,因此强烈建议使用token_compress_on
ForwardElem* BuildForwardIndex(const std::string& line)
{//line:title\3content\3\urlstd::vector results;const std::string sep = "\3";ns_util::StringUtil::Split(line,&results,sep);//根据sep切分字符串。//results为:[0]title、[1]content、[2]urlif(results.size() != 3)//不为3则出错处理{return nullptr;}ForwardElem fe;fe.title = results[0];fe.content = results[1];fe.url = results[2];fe.id = forward_index.size();//一开始size()为0forward_index.push_back(std::move(fe));//move是减少拷贝的操作return &forward_index.back();//将fe返回给倒排索引,建立倒排索引。//注意:这里不能用&fe,因为上面用了move(),这是一个大坑
}
编写BuildInvertedIndex()函数
该函数的需要对DocInfo正排文档进行title和content的分词来建立倒排索引,这里我使用的是cppjieba分词。
第一步:
安装cppjieba网址:https://github.com/yanyiwu/cppjieba
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-TXXTRAmp-1677284957538)(BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目.assets/image-20230224164636720.png)]](/uploadfile/202405/93db9e3a6cc15.png)
然后git clone下来即可
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-UW1K7Hi9-1677284957538)(BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目.assets/image-20230224165137692.png)]](/uploadfile/202405/fee89ab11fcd2e4.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Msi1eE1O-1677284957539)(BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目.assets/image-20230224165208995.png)]](/uploadfile/202405/3fbb20b71703738.png)
其中include/cppjieba包含我们需要的.h头文件,但这里有个小bug,需要将deps/limon目录拷贝到include/cppjieba目录下才能正常使用。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5rIfTvxL-1677284957540)(BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目.assets/image-20230224165449159.png)]](/uploadfile/202405/e98b5c312521024.png)
现在我们开始使用cppjieba中的test文件进行小测试
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-DqKBLBm3-1677284957541)(BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目.assets/image-20230224165631541.png)]](/uploadfile/202405/338539e59416277.png)
用vim打开这个demo.cpp看看情况
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-m4alw5we-1677284957541)(BoostSearcher搜索引擎项目.assets/image-20230224165718546.png)]](/uploadfile/202405/95de5443eaf0781.png)
由于我把demo.cpp拷贝到了另外一个目录,这里面使用的相对路径就都失效了,需要我们解决。同时还需要包含、等头文件。
如何解决相对路径失效的问题?
答案:使用软连接解决。
如下:
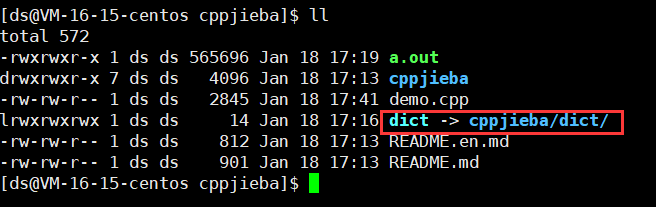
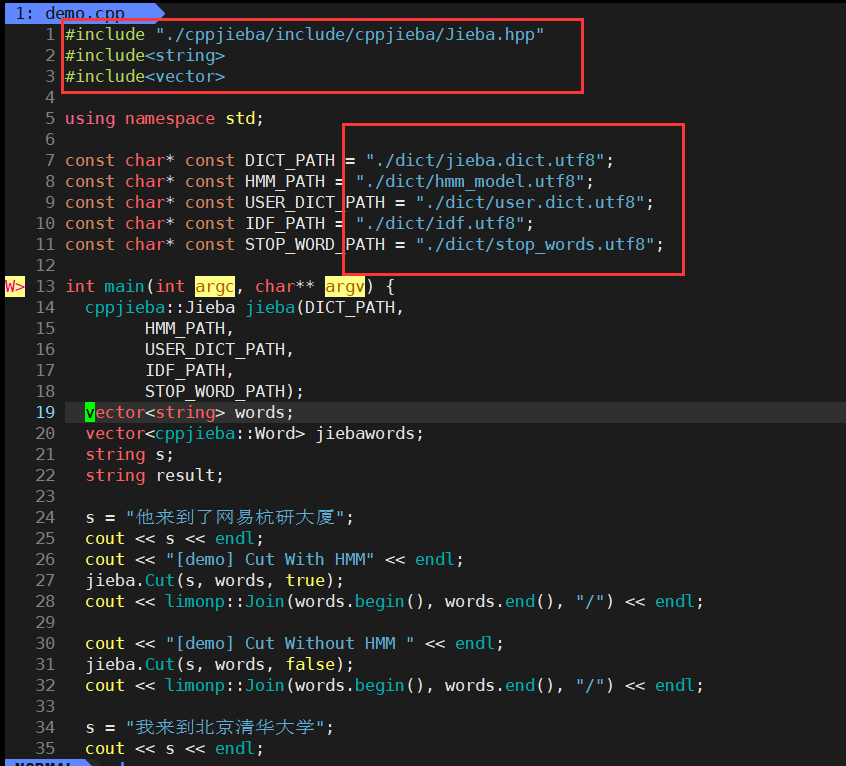
然后就可以通过g++编译运行demo.cpp了

搞定cppjieba分词组件后,我们需要把它放到一个指定路径下,作为项目的第三方库路径,这样项目看起来更工程点。
比如~/third-lib
使用时通过软连接引用即可。
接下来我们需要用cppjieba完成一个易于调用的分词函数,我把它写到了工具类中。
namespace JiebaUtil
{//下面5行都是用于分词的词库const char* const DICT_PATH = "./dict/jieba.dict.utf8";const char* const HMM_PATH = "./dict/hmm_model.utf8";const char* const USER_DICT_PATH = "./dict/user.dict.utf8";const char* const IDF_PATH = "./dict/idf.utf8";const char* const STOP_WORD_PATH = "./dict/stop_words.utf8";cppjieba::Jieba jieba(DICT_PATH,HMM_PATH,USER_DICT_PATH,IDF_PATH,STOP_WORD_PATH);std::unordered_map stop_words;void CutString(const std::string& line,std::vector* out)//完成分词函数{jieba.Cut(line,*out);}
}
以后我们只需要调用工具类中的CutString即可完成分词。
分词工具搞定后,接下来我们需要完成的是BuildInvertedIndex函数的编写,这个函数是重点中的难点。
bool BuildInvertedIndex(const ForwardElem& fe)
{struct word_cnt//记录某个关键字在title中出现次数和在content中出现次数。{int title;int content;word_cnt():title(0),content(0){};};std::unordered_map word_map;//词频统计//对title进行分词std::vector title_words;ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(fe.title,&title_words);//统计title词频for(auto word : title_words)//这里需要用传值,否则会改变title_words{boost::to_lower(word); //将word转化为小写,全部建立小写的索引,查询时转换成小写再查询索引word_map[word].title++;}//对content进行分词std::vector content_words;ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(fe.content,&content_words);//统计content词频for(auto word : content_words){boost::to_lower(word);//将word转化为小写,全部建立小写的索引,查询时转换成小写再查询索引word_map[word].content++;}#define X 10
#define Y 1for(auto& word : word_map){InvertedElem ie;//构建倒排文档ie.id = fe.id;//这是为什么DocInfo结构体为什么有id成员变量的原因,方便构建InvertedElemie.weight = X * word.second.title + Y * word.second.content;//权重设置ie.word = word.first;//设置关键字InvertedList& iel = inverted_index[ie.word]; //将相同关键字的倒排文档插入至倒排拉链iel.push_back(std::move(ie));//构建关键字和倒排拉链的映射}return true;
}
终于完成了Index.hpp的编写,但还有一点完善的是,为了项目的工程性,我们需要把index.hpp设置成单例模式
#pragma once #include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include"util.hpp"
#includenamespace ns_index
{struct ForwardElem{std::string title;std::string content;std::string url;uint64_t id;};struct InvertedElem{uint64_t id;int weight;std::string word;};typedef std::vector InvertedList;class Index{private:std::vector forward_index;std::unordered_map inverted_index;private:static Index* instance;static std::mutex mtx;Index(){};Index(const Index&) = delete;Index& operator=(const Index&) = delete;public:~Index(){};public:static Index* GetInstance(){if(instance == nullptr){mtx.lock();if(instance == nullptr){instance = new Index();}mtx.unlock();}return instance;}ForwardElem* GetForwardIndex(uint64_t id){if(id > forward_index.size()){std::cerr<<"id index beyond range"<second;}bool BuildIndex(const std::string& raw_path){std::ifstream ifs(raw_path,std::ios::in | std::ios::binary);if(!ifs.is_open()){std::cerr< results;const std::string sep = "\3";ns_util::StringUtil::Split(line,&results,sep);if(results.size() != 3){return nullptr;}ForwardElem fe;fe.title = results[0];fe.content = results[1];fe.url = results[2];fe.id = forward_index.size();forward_index.push_back(std::move(fe));return &forward_index.back();//注意:这里不能用&fe,因为上面用了move()}bool BuildInvertedIndex(const ForwardElem& fe){struct word_cnt{int title;int content;word_cnt():title(0),content(0){};};std::unordered_map word_map;//对title进行分词std::vector title_words;ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(fe.title,&title_words);//统计title词频for(auto word : title_words){boost::to_lower(word); word_map[word].title++;}//对content进行分词std::vector content_words;ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(fe.content,&content_words);//统计content词频for(auto word : content_words){boost::to_lower(word);word_map[word].content++;}#define X 10
#define Y 1for(auto& word : word_map){InvertedElem ie;ie.id = fe.id;ie.weight = X * word.second.title + Y * word.second.content;ie.word = word.first;InvertedList& iel = inverted_index[ie.word]; iel.push_back(std::move(ie));}return true;}};Index* Index::instance = nullptr;std::mutex Index::mtx;
}
6.3为用户提供搜索服务
思路:先写本地的Search服务,再转为网络服务。
本地服务:Search.hpp
#pragma once #include
#include
#include
#include
#include"index.hpp"
#includenamespace ns_searcher
{struct InvertedInfoPrint{uint64_t id;int weight;std::vector words;InvertedInfoPrint():id(-1),weight(0){};};class Searcher{private:ns_index::Index* index;//索引服务public:void InitSearcher(const std::string& input)//初始化Searcher{index = ns_index::Index::GetInstance();std::cout<<"获取单例成功!"<BuildIndex(input);std::cout<<"构建索引成功!"< words;ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(query,&words);//对query进行分词std::unordered_map for_unique;//对倒排文档去重而创建std::vector InvertedList_all;//新的倒排拉链for(auto& word : words){boost::to_lower(word);//查找索引前需要转为小写,因为索引的关键字都是小写的ns_index::InvertedList* list = index->GetInveredList(word);//获取倒排拉链if(list == nullptr){continue;}for(auto& item : *list)//对组合的倒排拉链进行去重{InvertedInfoPrint& ele = for_unique[item.id];ele.id = item.id;ele.weight += item.weight;//相同文档,权重相加ele.words.push_back(item.word);}}for(const auto& e : for_unique)//得到新的倒排拉链{InvertedList_all.push_back(std::move(e.second));//}std::sort(InvertedList_all.begin(),InvertedList_all.end(),\[](const InvertedInfoPrint& e1,const InvertedInfoPrint& e2){return e1.weight > e2.weight;});//对新的倒排拉链进行权重降序排序//完成序列化与反序列化Json::Value root;for(auto& e : InvertedList_all)//根据倒排文档得到正排文档{ns_index::ForwardElem* fe = index->GetForwardIndex(e.id);//查找正排索引if(fe == nullptr){continue;}Json::Value ele;ele["title"] = fe->title;ele["desc"] = GetDesc(fe->content,e.words[0]);//根据内容得到摘要,这里是为什么InvertedEle中有word成员变量的原因。ele["url"] = fe->url;root.append(ele);}Json::FastWriter w;*json_string = w.write(root);}//摘要设计:找到word出现在content的第一个位置,向前找50个字符,再向后找100个字符构成摘要。如果前面不够50个,则从0下标开始截取。如果后面不够100个,则截取到结尾。std::string GetDesc(const std::string& content,const std::string& word){const int prev = 50;const int next = 100;//这里有一个大坑,不能使用string.find()查找,因为它不能忽略大小写查找。如果你查找的是filesystem,则找到的只有filesystem。auto iter = std::search(content.begin(),content.end(),word.begin(),word.end(),\[](int x,int y){return std::tolower(x) == std::tolower(y);});if(iter == content.end()){return "None1";}int pos = std::distance(content.begin(),iter);//得到找到位置的下标int start = 0;int end = content.size()-1;if(pos-prev > start){start = pos-prev;}if(pos + next < end){end = pos + next;}if(start > end){return "None2";}std::string desc = content.substr(start,end-start);desc += "....";return desc;}};
} 提供本地服务:
#include"searcher.hpp"const std::string input = "./data/raw/raw.txt";
char buf[256] = {0};
std::string query;
std::string json_string;int main()
{ns_searcher::Searcher s;s.InitSearcher(input);std::cout<<"Please Enter Your Query# ";fgets(buf,sizeof(buf)-1,stdin);//注:fgets会读取\n给buf。buffer[strlen(buffer)-1] = 0;//去掉buf里面的\nquery = buf;s.Search(query,&json_string);std::cout<提供网络服务:
这里使用现成的http服务:cpphttp-lib
编写http_server.cc
#include"searcher.hpp"
#include"cpp-httplib/httplib.h"
#include
#include"log.hpp"const std::string input = "./data/raw/raw.txt";
const std::string root_path = "./www.root";int main()
{ns_searcher::Searcher searcher;//创建serachersearcher.InitSearcher(input);//初始化searcherdaemonize();//将服务守护进程化Log log;log.enable();//设置日志httplib::Server svr;svr.set_base_dir(root_path.c_str());//设置web根目录svr.Get("/s",[&searcher](const httplib::Request& req,httplib::Response& res){if(!req.has_param("word"))//查看url是否携带word{res.set_content("必须要有搜索关键字","text/plain; charset = utf-8");//响应报文return;}std::string word = req.get_param_value("word");//获取word的value值std::string json_string;searcher.Search(word,&json_string);//获取Json字符串res.set_content(json_string,"application/json");//将Json串返回给客户端});std::cout<<"服务启动成功!!"< 将http_server.cc守护进程化
#pragma once#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include void daemonize()
{int fd = 0;// 1. 忽略SIGPIPEsignal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);// 2. 更改进程的工作目录// chdir();// 3. 让自己不要成为进程组组长if (fork() > 0)exit(1);// 4. 设置自己是一个独立的会话setsid();// 5. 重定向0,1,2if ((fd = open("/dev/null", O_RDWR)) != -1) // fd == 3{dup2(fd, STDIN_FILENO);dup2(fd, STDOUT_FILENO);dup2(fd, STDERR_FILENO);// 6. 关闭掉不需要的fdif(fd > STDERR_FILENO) close(fd);}
}
6.4编写前端代码
这里的前端代码看看就行,主要是为了展示项目。
boost 搜索引擎
6.5日志的补充
编写log.hpp
#pragma once#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include #define DEBUG 0
#define NOTICE 1
#define WARINING 2
#define FATAL 3const char *log_level[] = {"DEBUG", "NOTICE", "WARINING", "FATAL"};#define LOGFILE "serverTcp.log"class Log
{
public:Log():logFd(-1){}void enable(){umask(0);logFd = open(LOGFILE, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0666);assert(logFd != -1);dup2(logFd, 1);dup2(logFd, 2);}~Log(){if(logFd != -1) {fsync(logFd);close(logFd);}}
private:int logFd;
};// logMessage(DEBUG, "%d", 10);
void logMessage(int level, const char *format, ...)
{assert(level >= DEBUG);assert(level <= FATAL);char *name = getenv("USER");char logInfo[1024];va_list ap; va_start(ap, format);vsnprintf(logInfo, sizeof(logInfo) - 1, format, ap);va_end(ap); // ap = NULLFILE *out = (level == FATAL) ? stderr : stdout;fprintf(out, "%s | %u | %s | %s\n",log_level[level],(unsigned int)time(nullptr),name == nullptr ? "unknow" : name,logInfo);fflush(out); // 将C缓冲区中的数据刷新到OSfsync(fileno(out)); // 将OS中的数据尽快刷盘
}
6.6项目扩展
- 建立全站搜索
- 设计一个在线更新的方案,信号,爬虫,完成整个服务器的设计
- 不使用组件,而是自己设计一下对应的各种方案
- 在我们的搜索引擎中,添加竞价排名
- 热次统计,智能显示搜索关键词(字典树,优先级队列)
- 设置登陆注册,引入对mysql的使用
上一篇:OpenAPI SDK组件介绍
下一篇:gin 框架初始教程文档